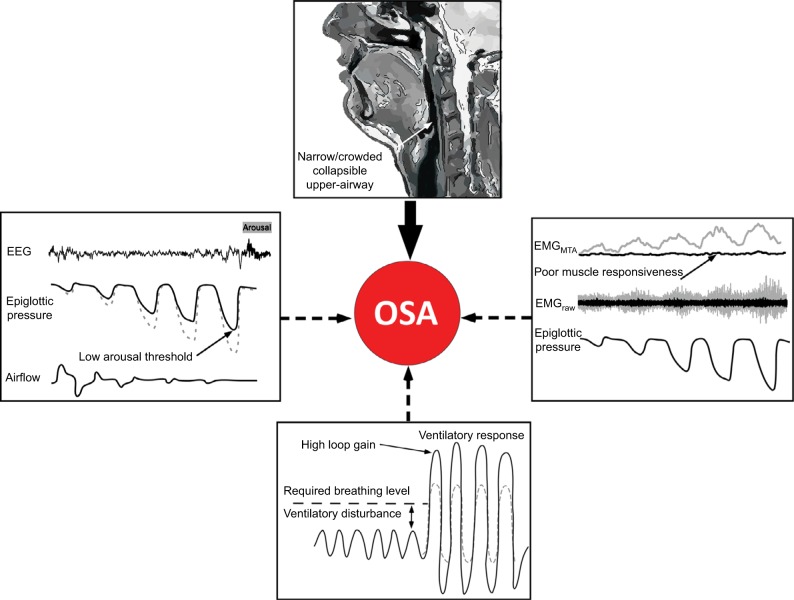
Figure 1.
Schematic of the anatomical and non-anatomical causes of OSA.
Notes: Some degree of anatomical vulnerability is present in OSA. However, the extent of impairment varies widely between patients. The non-anatomical contributors, which are present in approximately 70% of OSA patients, play a key role in mediating the absence or presence of OSA. In the schematic, the gray tracings indicate the desired response, whereas the black tracings represent impairment in the non-anatomical trait. Refer to the text for further detail. Reprinted from Chest, Carberry JC, Amatoury J, Eckert DJ, Personalized management approach for OSA, Epub 2017 June 16, Copyright (2017), with permission from Elsevier.36
Abbreviations: EEG, electroencephalography; EMG, genioglossus electromyography; MTA, 100 ms moving time average of the rectified raw EMG signal; OSA, obstructive sleep apnea.