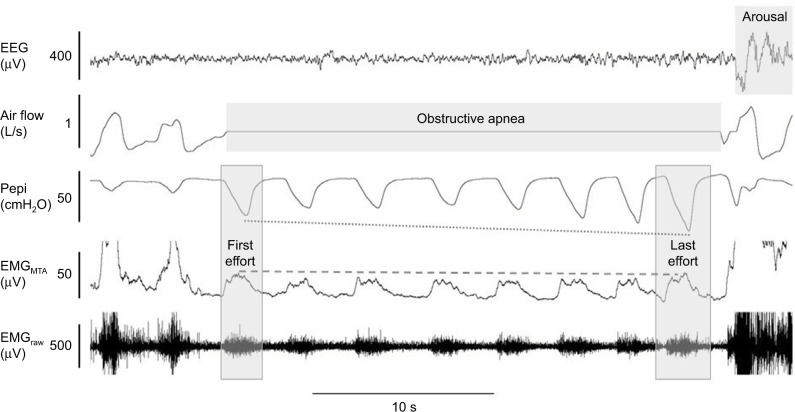
Figure 2.
Example of minimal genioglossus muscle responsiveness.
Notes: In this example of a naturally occurring apnea, despite clear phasic activation of the genioglossus muscle (as shown in the raw and MTA genioglossus EMG channels), there is minimal activation of genioglossus during the respiratory event. This is despite substantial increasing negative epiglottic pressure (Pepi) swings from the first to last effort (last effort nadir epiglottic pressure = arousal threshold). It is only when cortical arousal occurs (as shown in the EEG channel) that major genioglossus activation occurs (signal clipped in this example) and airflow is restored.
Abbreviations: EEG, electroencephalography; EMG, genioglossus electromyography; MTA, 100 ms moving time average of the rectified raw EMG signal.