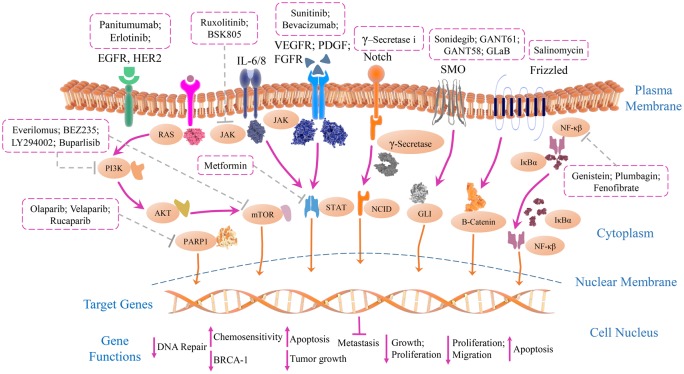
Figure 1. Overview of signalling pathways involved with identified potential inhibitors in TNBC.
The network of multiple signalling cascades with downstream effectors help in the maintenance of growth, proliferation, survival and metastasis of TNBC cells. The signalling pathways like NF-κB, PI3/AKT/mTOR, JAK/STAT and RTKs (receptor tyrosine kinases) are implicated in the pathogenesis of TNBC cells. The developmental pathways like Wnt/β-Catenin, Notch, Hh (Hedgehog) are associated with invasion, migration, metastatic potential and also self-renewal ability of cancer stem cells. PARP inhibitors directly interact and inhibit molecules associated with DNA repair to increase the cellular damage ultimately leading to apoptosis. Most of the potential inhibitors directly induced apoptosis in TNBC by up-regulation of Bad, Caspase 3 and down-regulation of BCL-2, BCL-XL and survivin. While several inhibitors showed therapeutic response through control of tumour growth and antiproliferative effect on TNBC cells, some inhibitors increased chemosensitivity of TNBC cells. So, synergistic targeting of chemotherapy drugs and therapeutic inhibitors may prove to be an effective way of treatment for TNBC.