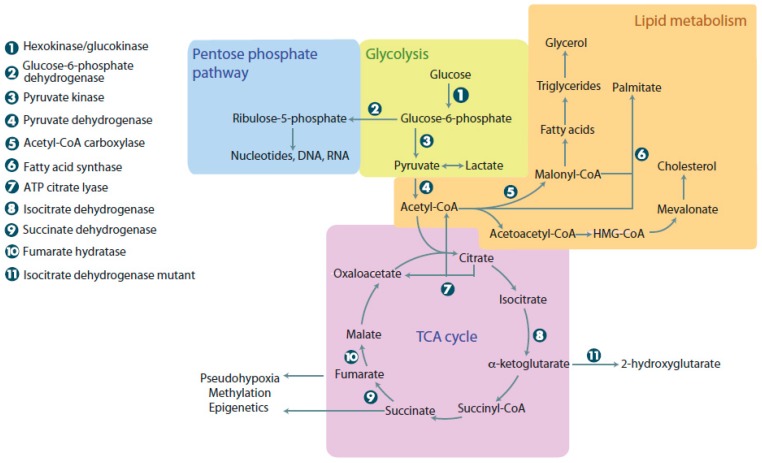
Figure 1.
Metabolic pathways in normal and cancer cells. When glucose enters cells, it undergoes glycolysis, linking it to the pentose phosphate pathway, lipid metabolism, and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. The pentose phosphate pathway can be used to make nucleotides, DNA, and RNA. Lipid metabolism is used for energy and synthesis of membrane components. The TCA cycle provides cells with intermediates for the electron transport chain and links many other metabolic reactions that occur in the cell. Cancer cells with mutations in metabolic enzymes have increased levels of 2-hydroxyglutarate, succinate, and malate, resulting in adverse cellular outcomes. ATP: Adenosine triphosphate.