Extended Data Figure 10. Genetic features of E×E CGI methylation in cancers.
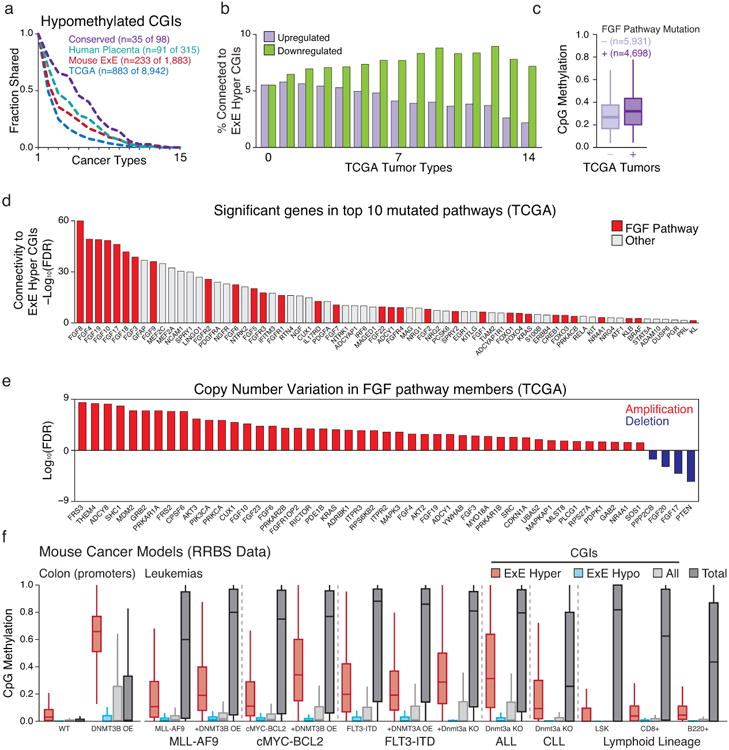
a. Intersection analysis as presented in Figure 4 for cancer-hypomethylated CGIs across the 14 TCGA tumor types and CLL that exhibit global loss of methylation in tandem with CGI hypermethylation. Generally, CGI hypomethylation is more specific, such that the intersection across cancers decays exponentially. Notably, even for hypomethylated CGI, the intersection across cancer types remains higher for those that are also hypomethylated in E×E, human placenta, or both (conserved).
b. Intersection analysis for cancer-dysregulated genes across TCGA tumor types. Of genes significantly dysregulated in at least n (0 – 14) TCGA cancer types, the fraction of genes that are functionally related to E×E Hyper CGI-associated genes were predicted by GRAIL, using a global gene-network built by text-mining (see Methods). An FDR of 5% was used as cutoff. As the number of TCGA tumor types increases, the fraction of E×E Hyper CGI-associated genes within the downregulated set generally increases, while those that are upregulated decreases substantially.
c. Boxplots of the average methylation for the 489 orthologous E×E Hyper CGI feature set for 10,629 tumors available in TCGA with matched mutational and methylation data, segregated by mutational status of genes that function as part of the FGF signaling pathway. In aggregate, tumors with FGF pathway mutations have a median average E×E Hyper CGI methylation level of 0.328 compared to 0.275 for those that do not (p<10-16, Rank Sum Test). Edges refer to the 25th and 75th percentiles, whiskers the 2.5th and 97.5th percentiles, respectively.
d. Among 539 genes that are present in the top 10 recurrently mutated pathways in cancer, 68 are functionally related to E×E Hyper CGI-associated genes (FDR < 5%), as predicted by GRAIL using text-mining database. Genes in FGF-signaling pathway are highlighted in red. In general, FGF signaling pathway genes have high connectivity scores to E×E hyper CGI-associated genes (Enrichment Z score = 3.88 for FGF pathway members within the p-value distribution for all 539 genes).
e. Statistical enrichment for FGF pathway genes for either amplification or deletion within the TCGA database is notably skewed towards amplification, indicating a generally oncogenic nature for this pathway in tumorigenesis.
f. Methylation status of E×E Hyper CGIs across colonic and hematopoietic mouse cancer models where de novo methyltransferase activity has been perturbed. All samples are measured by RRBS. Data sets include: primary colon tissue in which Dnmt3b has been overexpressed (promoter methylation status reported, Ref 62); genetic models of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) including those transformed by the MLL-AF9 fusion (Ref 63), cMyc and Bcl2 overexpression (Ref 63), and FLT3 internal tandem duplication (FLT3-IDT, Ref 64); and Acute and Chronic Lymphoblastic Leukemia models driven by Dnmt3a knock out alone (Refs 65 and 66). Methylation of E×E Hyper CGIs is observed in both colonic Dnmt3b overexpression and hematopoietic Dnmt3a knockout, though additional oncogenic drivers appear sufficient to induce de novo methylation of these regions in the presence or absence of Dnmt3 expression, indicating the potential of numerous drivers to activate this pathway. Wild type hematopoietic tissues are included for reference and taken from Ref 65 and 66. Edges refer to the 25th and 75th percentiles, whiskers the 2.5th and 97.5th percentiles, respectively.
