Figure 2. De novo methylation of early developmental gene promoters can be modulated by external conditions.
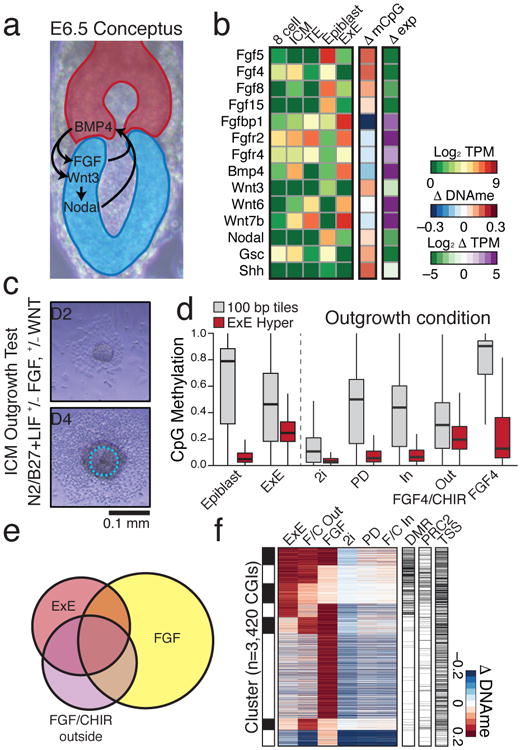
a. Schematic of signaling pathway interactions between Epiblast (blue) and E×E (red). Epiblast-produced Fibroblast Growth Factors (FGFs) promote E×E development, which expresses Bone Morphogenic Protein 4 (BMP4) to induce Wingless (WNT) proteins in Epiblast. Epiblast secreted pro-Nodal is processed by the E×E to establish a proximal-distal gradient and the primitive streak10.
b. Expression and differential promoter methylation of key signaling components. Many FGFs and associated receptors exhibit reciprocal expression and promoter methylation between Epiblast and E×E. Wnt3 induction is apparent in epiblast, while Wnt6 and 7b are highly expressed in both TE and E×E. Differential promoter methylation refers to the annotated TSS (+ or – 1 kb) with the greatest absolute difference (Supplementary Table 2).
c. Schematic for the ICM outgrowth test. ICM outgrowths are cultured for 4 days under disparate growth factor or small molecule conditions intended to either stimulate or repress FGF and WNT activity. Outline highlights the purified component (Methods).
d. Methylation boxplots for the conditions described in c, including all RRBS-captured 100 bp tiles and E×E-targeted CGIs (E×E Hyper CGIs). Edges refer to the 25th and 75th percentiles, whiskers the 2.5th and 97.5th percentiles, respectively.
e. The E×E, FGF/CHIR exterior, and FGF outgrowth all display substantial CGI methylation. Shown is the intersection of methylated CGIs with ≥0.1 increase in comparison to Epiblast (n=3,420). The FGF4 condition has the highest number of methylated CGIs, but fewer intersect with E×E than when CHIR is also present.
f. Clustering of differentially methylated CGIs from e, with methylation status in E×E, embryonic regulation by PRC2, and TSS proximity (+/- 2 kb) included. 25% of E×E methylated CGIs overlap with both conditions, while 51% overlap with the FGF/CHIR exterior outgrowth.
