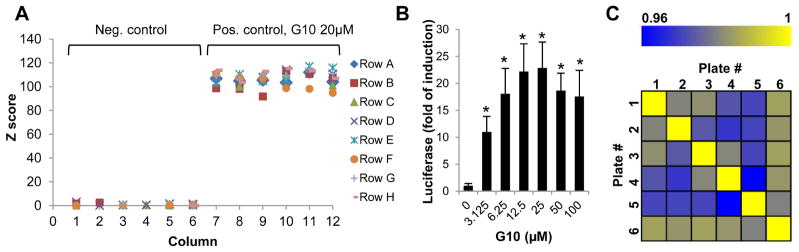
Figure 3. Characterization of high throughput assay using control plates and hypothetical replicate plates.
(A) In each batch of experiment, a plate of HepAD38/cGAS-STING/ISG54Luc cells was used as control plate with 6 columns of the wells treated with 2% DMSO (n=48) and 6 columns of the wells treated with 20μM of reference compound G10 (n=48). The firefly luciferase activities were measured in parallel with all the other test plates at 4 h post treatment. The Z scores were calculated and shown for a representative control plate. (B and C) HepAD38/cGAS-STING/ISG54Luc cells were seeded in 6 of 96-well plate. Each plate had 6 columns of the wells treated with 2% DMSO (n=48 per plate) and the other columns of the wells treated with 6 increasing concentrations of G10 (n=8 per dose, per plate). The average luciferase value in treated wells relative to control wells (fold of induction) were calculated from 6 plates, and expressed as mean ± standard deviation. * indicates p<0.05 compared to mock treated control (B). Pairwise Pearson’s coefficient of data on 6 hypothetical replicate plates was shown in a correlation heat map (C).