Fig. 2.
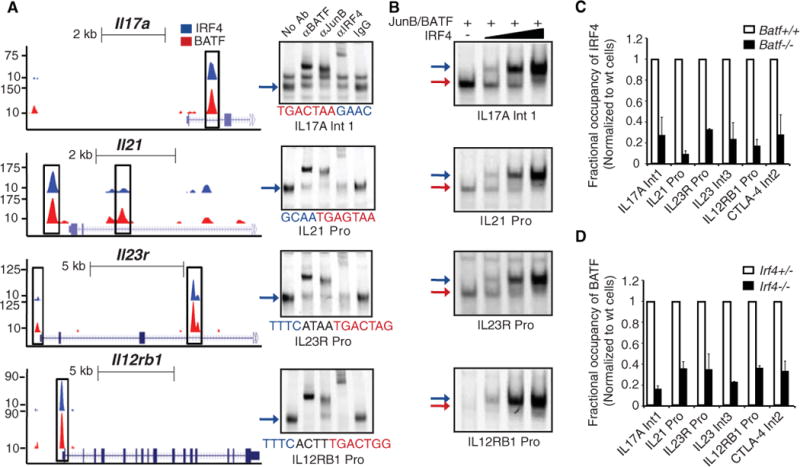
IRF4-BATF-JunB complexes assemble on presumptive regulatory sequences in key TH17 genes. (A) (Left) ChIP-seq tracks for IRF4 (blue) or BATF (red) at the Il17a, Il21, Il23r, and Il12rb1 loci. Coincident peaks containing AICE motifs are highlighted (boxed regions). (Right) EMSAs using nuclear extracts from TH17 cells and the indicated DNA probes and antibodies. (B) EMSAs using nuclear extracts from 293T cells overexpressing indicated proteins. Reactions were performed with increasing amounts (fivefold) of IRF4 protein. (C) ChIP analysis of IRF4 binding on indicated sequences in wild-type and Batf−/− T cells. (D) ChIP analysis of BATF binding on indicated sequences in Irf4+/− and Irf4−/− T cells. Purified CD4 cells were polarized for 42 hours under TH17 differentiating conditions. The average ± SD of two independent experiments is shown for each target sequence after normalization to control T cells.
