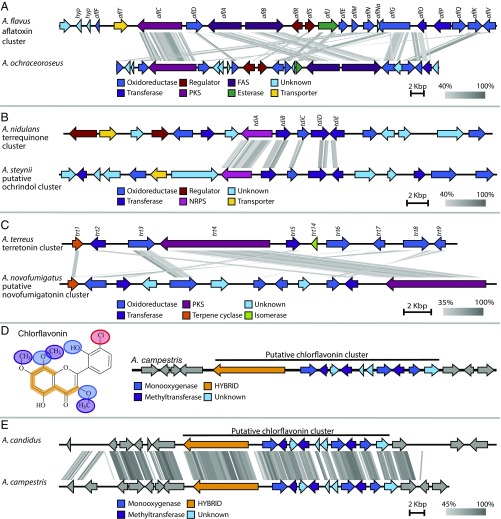
Fig. 3.
Synteny plots of investigated clusters made using Easyfig tBLASTx. (A) The synteny of the predicted aflatoxin cluster in A. flavus NRRL3357 and the identified candidate aflatoxin cluster in A. ochraceoroseus (scaffold 2, 4,201,774–4,251,209 bp). (B) Synteny plot of the candidate cluster for ochrindol in A. steynii (scaffold 7, 2,783,445–2,824,507 bp) and terrequinone cluster in A. nidulans. The terrequinone cluster consists of a single-module nonribosomal peptide synthetase (tdiA), a prenyltransferase (tdiB), an oxidoreductase (tdiC), an aminotransferase (tdiD), and a gene of unknown function similar to a methyl transferase (tdiE). (C) Synteny plot of the known meroterpenoid cluster of terretonin in A. terreus and the candidate cluster of novofumigatonin in A. novofumigatus (scaffold 14, 103,246–136,450 bp). (D) The chemical structure of chlorflavonin and the candidate cluster for chlorflavonin in A. campestris (scaffold 1, 576,100–603,958 bp). The hydroxylation has been highlighted with blue, the O-methylation has been highlighted in purple, and the PKS backbone has been highlighted in orange. (E) Synteny plot of putative chlorflavonin clusters in A. candidus and A. campestris.