Introduction
Dupilumab is the first targeted biologic therapy approved for the treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD).1 More than 1,000 adult patient exposures formed the basis of its approval in March 2017 for the treatment of moderate-to-severe AD not well controlled with topical therapies or when other therapies are inadvisable. A reassuring safety profile was established, with conjunctivitis being the most significant safety signal.2 We describe our experience in a patient treated with dupilumab for AD that developed alopecia areata (AA) within 5 weeks of first exposure (3 doses).
Case report
A 29-year-old Indian male with no significant medical history presented with a 3-year history of poorly controlled, biopsy-proven AD. He was treated previously with phototherapy, topical corticosteroids, methotrexate, cyclosporine, and tofacitinib with only mild improvement. The patient's AD had a clinically psoriasiform appearance, and, because it was nonresponsive to treatment for AD, trials of prednisone, ustekinumab, apremilast, and secukinumab were implemented later in the treatment course (Table I). Prednisone induced osteopenia, ustekinumab resulted in generalized pruritus, and apremilast resulted in diarrhea. Tofacitinib helped partially. Workup for these medications yielded a positive γ-interferon release assay, prompting the successful completion of a 12-week course of weekly isoniazid, 600 mg, and rifapentine, 900 mg.3
Table I.
Timeline of failed therapies secondary to poor response or complication before dupilumab
| Date of therapy | Therapy |
|---|---|
| Before 7/18/16 | Methotrexate, cyclosporine, tofacitinib, topical corticosteroids |
| 7/18/2016–7/26/2016 | Cyclosporine |
| Before first appointment–11/22/2016 | Prednisone |
| 7/26/2016–8/30/2016 | Adalimumab |
| 8/16/2016–9/15/2016 | Ustekinumab |
| 8/30/2016–9/15/2016 | Apremilast |
| 10/11/2016–4/5/2017∗ | Secukinumab |
Secukinumab was discontinued and dupilumab was initiated 4/5/2017.
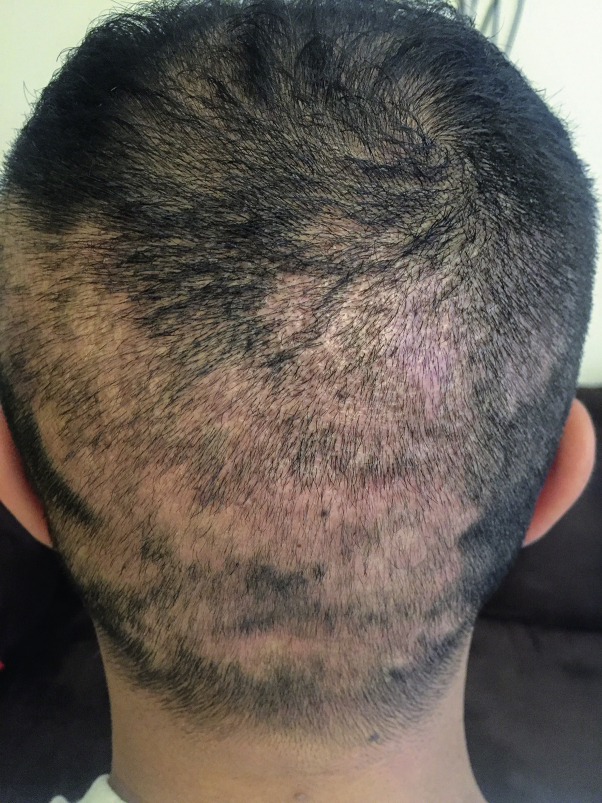
After it was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration, he was started on dupilumab at 600 mg subcutaneously on day 0 followed by 300 mg subcutaneously every 2 weeks beginning on day 15. After 6 weeks of treatment, his AD improved significantly; however, he noted several patches of hair loss on his posterior scalp that appeared after 5 weeks of treatment (Fig 1). He was seen in our clinic, and AA was diagnosed clinically (no biopsy was taken). He is currently being treated with intralesional triamcinolone acetonide, 5 mg/mL every 4 weeks, and his AA is gradually improving.
Fig 1.
Development of AA during dupilumab treatment. Clinical photograph of AA after 5 weeks of treatment with dupilumab and before treatment with intralesional triamcinolone acetonide, 5 mg/mL.
Discussion
We report a temporal relationship between dupilumab and the subsequent development of AA. Of course, temporal cannot be interpreted as causal; however, we cannot rule out this possibility. Reports of AA in patients on dupilumab therapy are absent in the existing medical literature. AA is commonly associated with atopic dermatitis.4 AD is primarily a type 2 T helper (Th2)-driven disease with increased interleukin (IL)-4, IL-5, IL-13, and IL-31.5 The pathogenesis of AA is not completely understood, but several studies found a heterogeneous process involving T-cell autoantigens, type 1 T helper (Th1)/interferon-γ, Th2, PDE4, IL-23, and IL-9.4 Because of the similar Th2 cytokine profile between AA and AD, dupilumab may actually be of clinical utility in AA and AD.4 Yet, the involvement of other immune system mediators, such as Th1, combined with the downregulation of Th2 pathways, may amplify the Th1 pathway and promote the development of AA with dupilumab use.4 As dupilumab moves into phase IV monitoring, clinicians will need to be aware of any potential adverse reactions that may arise. Despite the associated complication of AA, our patient remains on therapy satisfied with the outcome dupilumab provides and reports overall improved quality of life.
Footnotes
Funding sources: None.
Conflicts of interest: Jacob Levitt has served on advisory boards for Regeneron, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Amgen, Genentech, and Pfizer and has been a consultant to Novartis. Krystal Mitchell has no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- 1.Chang H.Y., Nadeau K.C. IL-4Ralpha inhibitor for atopic disease. Cell. 2017;170(2):222. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.06.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Shirley M. Dupilumab: first global approval. Drugs. 2017;77(10):1115–1121. doi: 10.1007/s40265-017-0768-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sterling T.R., Villarino M.E., Borisov A.S. Three months of rifapentine and isoniazid for latent tuberculosis infection. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2155–2166. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1104875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Revert-Yuval Y., Guttman-Yassky E. The changing landscape of alopecia areata: the therapeutic paradigm. Adv Ther. 2017;34(7):1594–1609. doi: 10.1007/s12325-017-0542-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Werfel R., Allam J., Biedermann T. Cellular and molecular immunologic mechanisms in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;138(2):336–349. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]