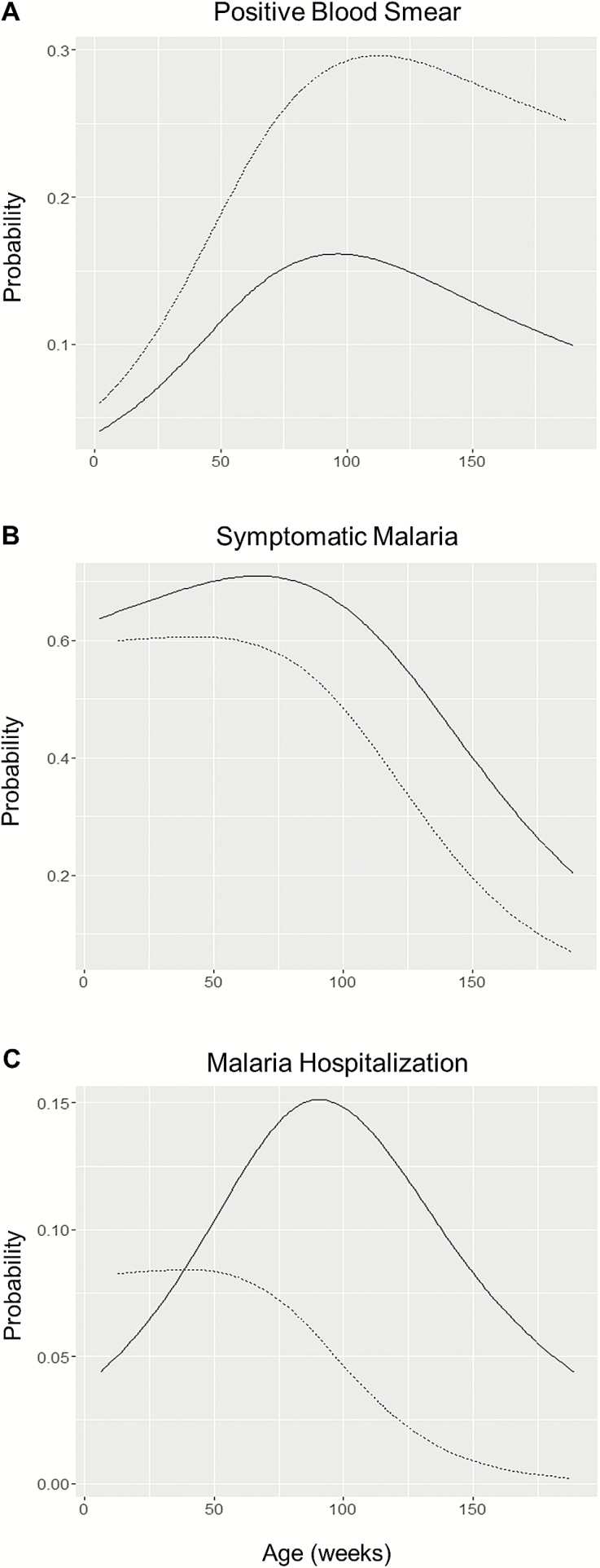
Figure 2.
Probability of malaria outcome by cord blood maternal microchimerism (MMc) detection. Offspring with no detectable MMc: n = 37; offspring with detectable MMc: n = 16. Solid line: no detectable MMc; dashed line: Detectable MMc. Age modeled as a cubic spline with 3 knots. A, MMc predicted increased risk of positive blood smear (BS) (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.73; P = .03). B, MMc predicted decreased risk of symptomatic malaria, given a positive BS (AOR, 0.47; P = .001). C, MMc predicted decreased risk of malaria hospitalization, given a positive BS (AOR, 0.41; P = .03).