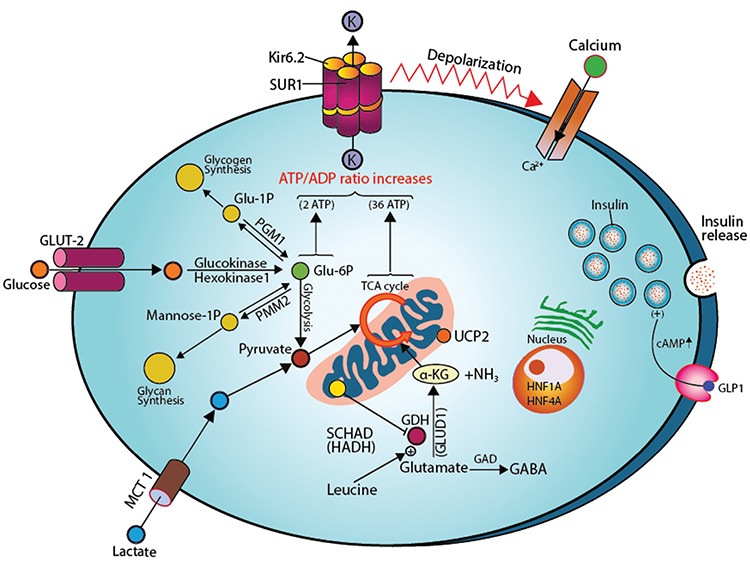
Figure 1. Regulation of insulin release from pancreatic β-cell and sites of gene mutations involved in the genetics etiology of hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia SUR1: sulphonlyurea receptor 1, Kir6.2: inwardly rectifying potassium channel 6.2, K: potassium, MCT1: monocarboxylate transporter 1, Glu: glucose, P: phosphorus; PGM1: phosphoglucomutase 1, PMM2: phosphomannose-mutase 2, UCP2: mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2, NH3: ammonia, GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase, GLUD1: glutamate dehydrogenase 1 gene, SCHAD: short-chain L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, HADH: hydroxy-acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, HNF1A and 4A: hepatocyte nuclear factor 1A and 4A, Ca+2: calcium; GAD: glutamate decarboxylase enzyme, GABA: γ-aminobutyric acid, GLP1: glucagon like peptide 1, cAMP: cyclic adenosine monophosphate (amplifier for the exocytosis of insulin secreting granule).