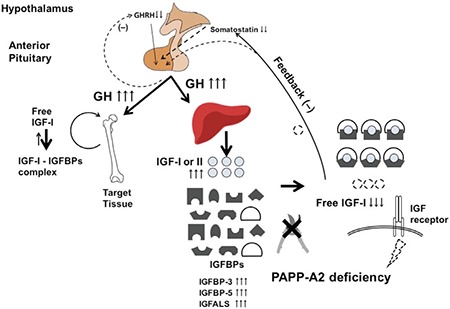
Figure 4. Schematic of the pathophysiology of loss of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A2 activity. The decreased or mutated pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A2 cannot proteolyze insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and -5 resulting in decreased free insulin-like growth factor-1. The reduction of free insulin-like growth factor-1 leads to increased growth hormone secretion due to a lack of negative feedback. Elevated growth hormone levels result in increased production of insulin-like growth factor-1 and -2 and insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Despite elevation of these hormones, insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling is decreased due to the low levels of free insulin-like growth factor-1 GH: growth hormone, IGF: insulin-like growth factor, IGFBP: insulin-like growth factor binding protein, GHRH: growth hormone-releasing hormone, PAPP-A2: pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A2.