Figure 4.
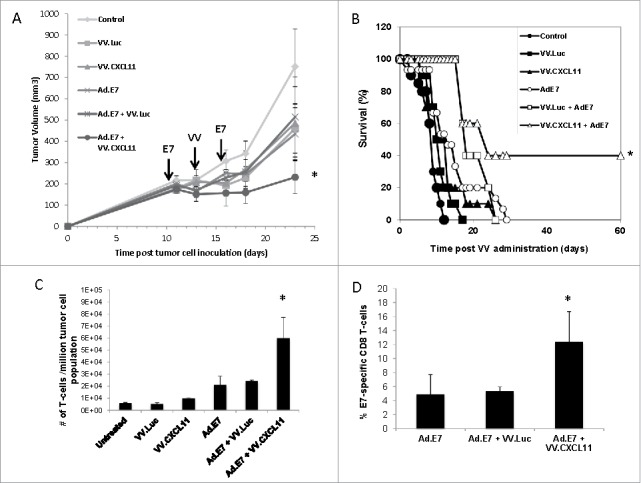
VV.CXCL11 significantly augmented an Ad.E7 cancer vaccine and increased T cell infiltration. A) TC1-bearing wild type mice were treated with Ad.E7 vaccine or vaccinia viruses – mice were vaccinated against E7 at Day 10 and again at Day 15, while vaccinia vectors were administered at Day 12. Tumor size was measured. Data shown are means ± SEM, n = 5 mice per group. A) Ad.E7 alone, VV.luc, VV.CXCL11, and Ad.E7 plus VV.luc all reduced the size of the TC1 tumors, but these changes did not reach statistical significance. In contrast, Ad.E7 plus VV.CXCL11 was the only group significantly smaller (p < 0.05) than control tumors. B) Survival curves from the same study, show that only the Ad.E7 plus VV.CXCL11 had prolonged survival (40%) (p < 0.05 using log-rank test). C) Tumors were harvested on Day 23. Ex vivo TIL analysis of tumors from each group revealed increased influxes of CD3 TILs in the Ad.E7 and Ad.E7 + VV.CXCL11 combination group. Data is expressed as means ± SEM, n = 5 mice per group (* = p < 0.05). D) The frequency of HPV-E7 positive CD8 TILs was determined. The percentage was significantly (p < 0.05) increased in the Ad.E7 + VV.CXCL11 combination group.
