Figure 5.
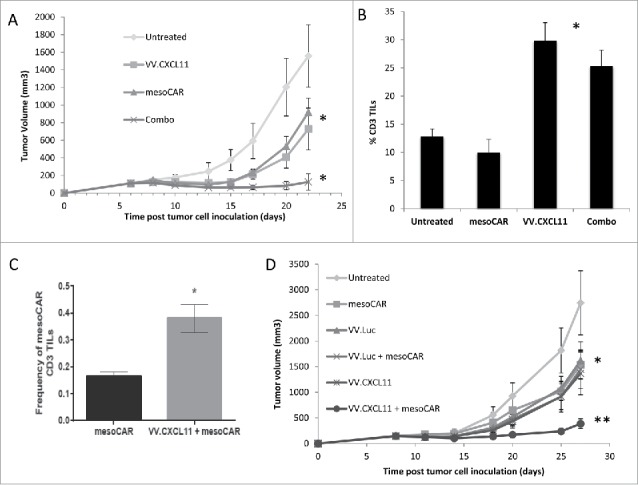
VV.CXCL11 significantly augmented mesoCAR immunotherapy. A) Mice bearing TC1-meso tumors were left untreated, injected iv with 108 pfu VV.CXCL11 on Day 5, injected iv with 107 mesothelin CAR-expressing T cells (iv) on day 8, or given both the iv VV.CXCL11 on Day 5 and the iv Meso-CAR T cells on Day 8. Tumor size was followed. Data is expressed as means ± SEM, n = 5 mice per group (* = p < 0.05). Both single treatments significantly (* = p < 0.05) reduced tumor size compared to control mice, however the combination was significantly (* = p < 0.05) more effective than either treatment alone. B) Tumors were digested and analyzed by flow cytometry on Day 22. The % of digested tumor cells that were CD3+ T cells was significantly higher in both groups receiving VV.CXCL11 (* = p < 0.05)). C) The % of adoptively transferred meso-CAR T cells present in the VV.CXCL11 treated tumors was more than double than that seen in the tumors treated with mesoCAR T cells alone (* = p < 0.05). D) In a separate experiment, groups received iv VV.luc alone and iv VV.luc plus iv Meso-CAR T cells in addition to the groups describe above in (A). Data is expressed as means ± SEM, n = 5 mice per group (* = p < 0.05). The combination of meso-CAR T cells plus VV.CXCL11 was again significantly better (p < 0.05) than all other treatments, however, administration of VV.luc did not augment the efficacy of Meso-CAR T cells. One way ANOVA with the appropriate post hoc testing, with * (P ≤ 0.05), ** (P ≤ 0.01). All experiments were replicated at least twice in an independent manner.
