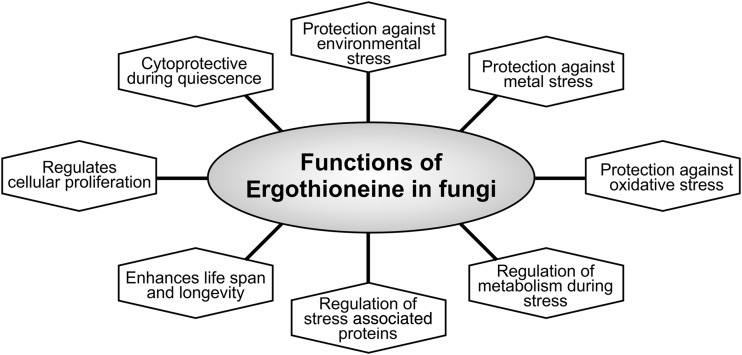
FIG. 8.
Functions of EGT in fungi. Schematic overview of the wide physiological functions played by ergothioneine in different fungal species. EGT has been shown to protect conidial germination, thereby enhancing the longevity and overall life span of N. crassa as well as in A. fumigatus. In N. crassa, along with its roles in longevity, EGT is also involved in maintaining cellular redox homeostasis. Similarly, in A. fumigatus, EGT is protective against oxidative stress contributed by free radicals and metal ions such as iron, cobalt, and copper. Furthermore, lack of EGT is also suggested to be responsible for the disruption of iron metabolism in A. fumigatus. In fission yeast, S. pombe, EGT protects the cells during quiescent stages and against environmental stresses, including nitrogen and glucose starvation, and heavy metal stress such as contributed by cadmium (Cd2+).