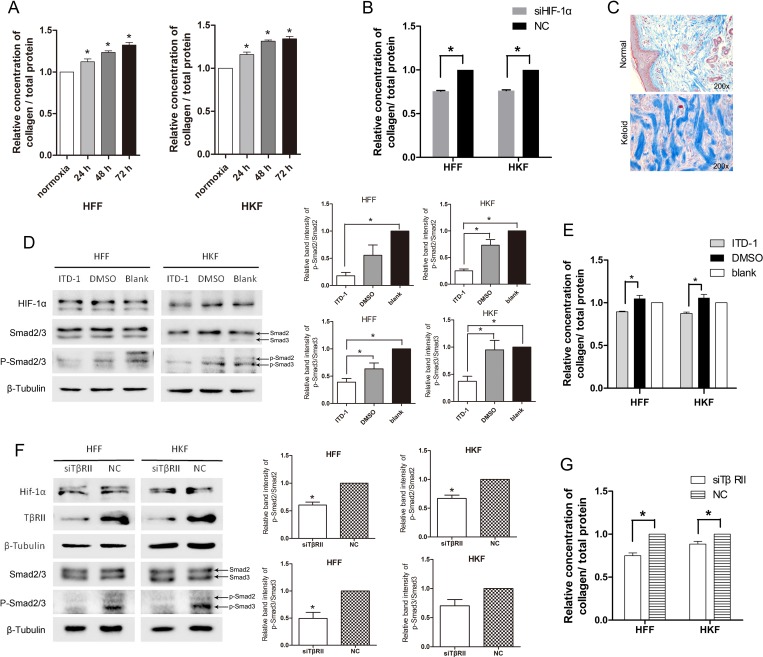
Figure 5. Total collagen deposition was promoted by acute hypoxia via HIF-1α and the TGF-β signaling pathway.
(A) The ratio of deposited collagen to the total protein concentration was elevated after 24 h, 48 h, 72 h of hypoxia in both HFFs and HKFs. (B) At 48 h after transfection, HFFs and HKFs were transferred to a 1% O2 hypoxia incubator for 24 h. Collagen deposition was clearly inhibited in the siHIF-1α group compared with the NC group. (C) Masson staining for collagen fiber (blue) of normal and keloid tissues. (D) Treatment with 5 μM ITD-1(dissolved in DMSO), DMSO, and blank, respectively, for 24 h under 1% O2 condition. ITD-1 inhibited the phosphorylation of Smad2/3 by inhibiting TβRII. Meanwhile, HIF-1α and Smad2/3 levels remained stable in all three groups. The histogram shows the protein band intensity ratio of p-Smad2 to Smad2 and p-Smad3 to Smad3. (E) Collagen deposition was reduced in the ITD-1-treated HFFs and HKFs. (F) siTβRII reduced the protein levels of TβRII, p-Smad2/3 at 72 h after transfection in normoxia. HIF-1α protein levels remained stable in the two groups. The histogram shows the protein band intensity ratio of p-Smad2 to Smad2 and p-Smad3 to Smad3. (G) Collagen deposition was clearly inhibited in the siTβRII group compared with the NC group.