Figure 1.
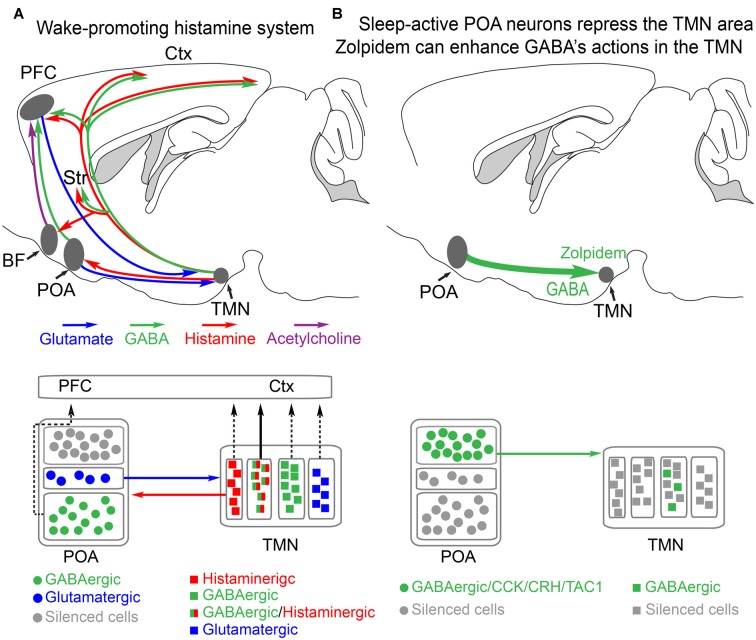
Histamine-GABA neurons in the tuberomammillary nucleus (TMN) area project widely to produce wakefulness and are silenced during NREM sleep by preoptic GABAergic neurons or by zolpidem. (A) Simplified view of how histamine/GABA neurons in the tuberomamillary area (TMN) of the posterior hypothalamus promote wakefulness. During the wake state, histamine/GABA neurons are active and their ascending histamine/GABA fibers release histamine (red) and GABA (green) into the prefrontal cortex (PFC), neocortex (Ctx) and striatum (Str, caudate-putamen). Glutamatergic pyramidal neurons in the PFC send excitatory projections to the histamine neurons in the TMN, reinforcing wakefulness. Histamine-only projections from the TMN also excite cholinergic neurons in the basal forebrain, and the axons of these excited cholinergic neurons release acetylcholine throughout the cortex. Histamine-only projections also excite GABAergic neurons in the preoptic area (POA) of the hypothalamus; these GABA neurons in turn are believed to supress sleep-active GABA neurons that project back to the TMN area that inhibit the histamine neurons. Within the POA, certain GABAergic cells project to the PFC and support wakefulness, and some glutamate cells in the POA also send excitatory projections to the histamine neurons to reinforce wakefulness. The TMN area also contains probably many wake-active glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons in addition to those that are histaminergic/GABAergic or histamine only. The contribution of these cells to wakefulness is not known. Based on Yu et al. (2015) and Chung et al. (2017). (B) During NREM sleep, the histaminergic neurons and probably some of the other cell types in the TMN area are inhibited by GABAergic projections (green) from the POA area. The GABAergic sleep active neurons probably co-release peptides, including CCK, CRH, TAC1 and galanin. The function of these peptides is not known. Zolpidem can also potentiate these GABAergic inputs via its actions at the postsynaptic GABAA receptors on histamine neurons. Adapted from Uygun et al. (2016).