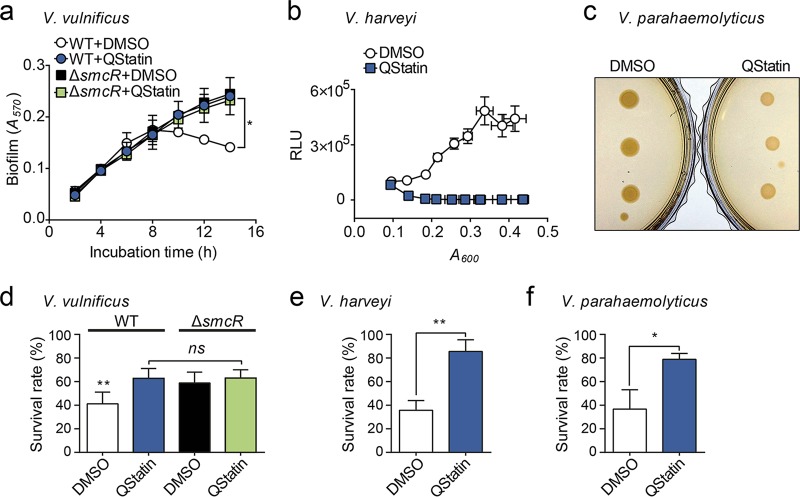
FIG 6 .
QStatin is a pan-QS inhibitor attenuating the virulence of pathogenic Vibrio species. (a) QStatin inhibits V. vulnificus biofilm dispersion. WT and ΔsmcR mutant strains were allowed to form biofilms in the presence of QStatin (20 μM) or DMSO (0.04%) for the indicated times at 30°C. Biofilm mass was then measured by crystal violet staining. Data are expressed as means ± SD of results from two independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA (*, P < 0.05). (b) QStatin inhibits V. harveyi bioluminescence. Early-exponential-phase V. harveyi cultures were transferred to microtiter plates, treated with QStatin (20 μM) or DMSO (2%), and further incubated at 30°C. Vertical and horizontal error bars represent the SD of the RLU and A600 values, respectively, from three independent experiments. (c) QStatin affects V. parahaemolyticus colony opacity. One microliter of an overnight V. parahaemolyticus culture was spotted onto LBS agar plates supplemented with QStatin (500 μM) or DMSO (2%). Three different cultures were spotted and monitored after growth at 30°C for 24 h. (d to f) Brine shrimp nauplii were challenged with V. vulnificus (d), V. harveyi (e), or V. parahaemolyticus (f) in the presence of QStatin (20 μM) or DMSO (0.04%). After 60 h, surviving shrimp were counted. Error bars represent the SD of the survival rates from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA (d) or Student’s t test (e and f) (**, P < 0.005; *, P < 0.05; ns, not significant).