FIG 6 .
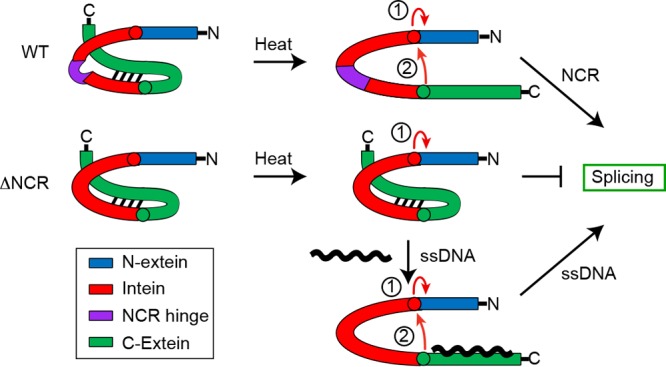
Model describing a role for the intein NCR in control of intein-extein interactions. Color coding of intein, N-extein, and C-extein is indicated in the key. Interactions between the intein and C-extein block splicing of the wild-type and ΔNCR RadA at low temperatures are shown. High temperatures can break these interactions in an NCR-dependent manner, whereby the NCR acts as a flexible hinge to switch on splicing. In contrast, ΔNCR maintains inhibitory intein–C-extein interactions. ssDNA, which accelerates and improves the accuracy of P. horikoshii RadA splicing, compensates for the absence of the NCR, interacting with the C-extein to break interactions with the intein, and promoting the catalytically competent state. The first two steps of the splicing reaction are indicated by red arrows (described in the text and the legend for Fig. 1A). We propose that step 2 of the reaction is blocked in the ΔNCR RadA protein in the absence of ssDNA.
