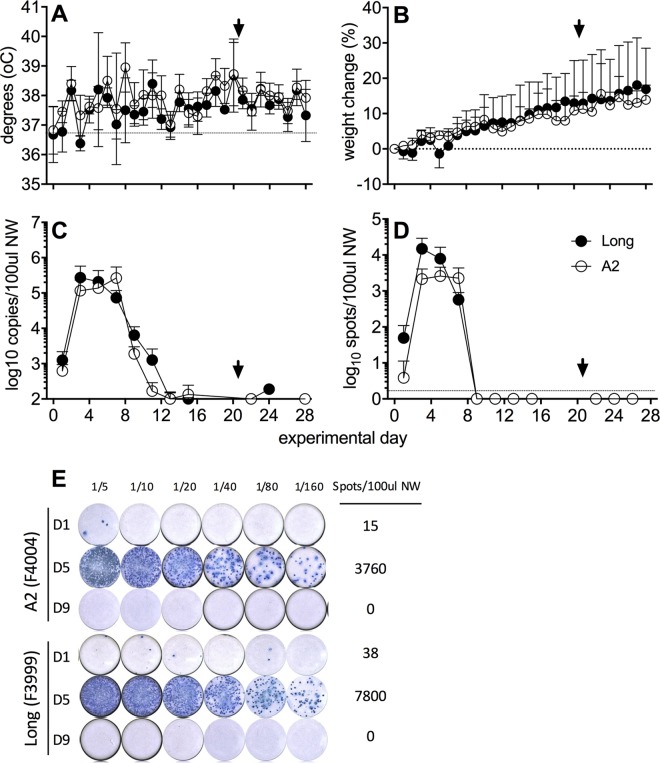
FIG 1.
Viral replication in the upper respiratory tract following experimental i.n. infection with hRSV. Ferrets (n = 4 per group) were infected i.n. with hRSV Long (closed circles) or A2 (open circles) virus, and NW samples were collected every second day. Temperature (A) and weight (B) were measured daily. (A and B) Means ± standard deviations from 4 ferrets per group are shown. (C) Viral shedding was quantified by real-time qPCR detection of the hRSV nucleoprotein (N) gene. (E) A ViroSpot (VS) assay was developed to measure titers of infectious virus in NW. Representative VS images of NW samples from two ferrets are shown at days 1, 5, and 9 p.i. (D) Titers of infectious virus in NW samples as determined by VS assay. Means ± standard deviations from 4 ferrets per group are shown in panels A and C. An arrowhead indicates reinfection with homologous virus strain. Statistical significance for virus shedding between viruses was analyzed by multiple t test with a Bonferroni-Dunn correction (alpha of 0.05), without assuming a consistent standard deviation. No significant differences were observed.