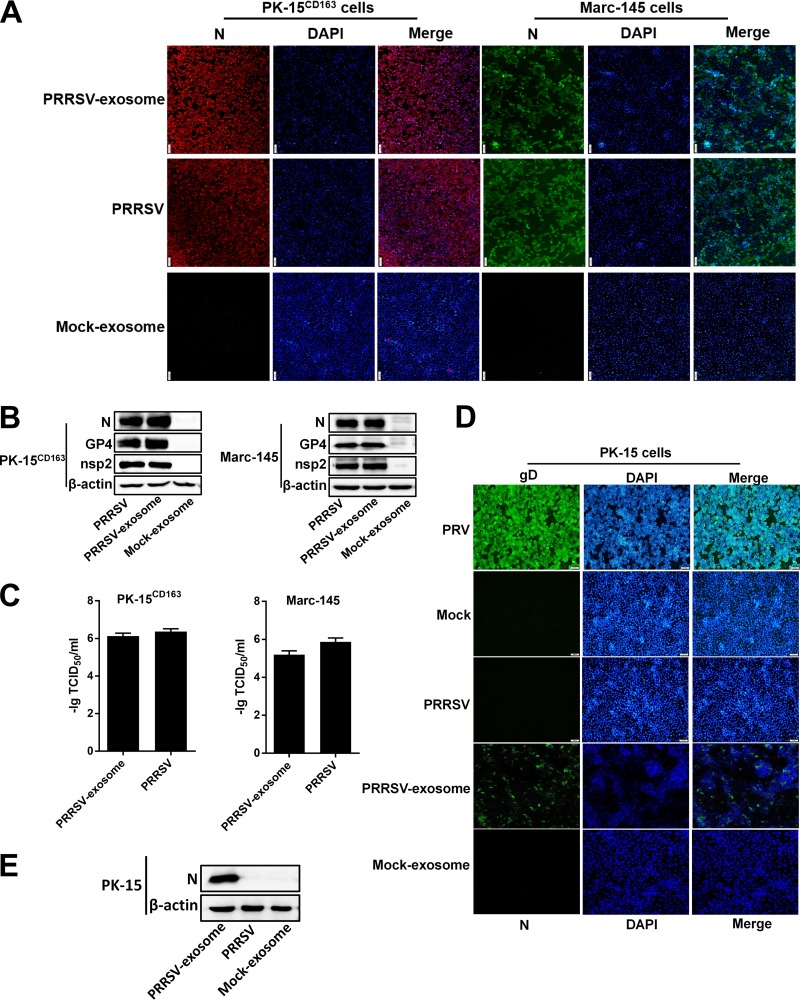
FIG 3.
Exosomes transmit PRRSV and establish productive infections in both susceptible and nonsusceptible cells. (A) IFAs demonstrated productive infection of Marc-145 and PK-15CD163 cells after treatment with PRRSV-positive exosomes. Marc-145 and PK-15CD163 cells were cocultured with PRRSV-positive exosomes or infected with PRRSV at an MOI of 1.0. At 36 h after treatment or infection, the cells were fixed and an IFA was performed with MAb directed against PRRSV N protein. Fluorescence was observed with an Olympus IX73 inverted microscope. (B) Western blot analysis of PRRSV N, GP4, and nsp2 expression in Marc-145 and PK-15CD163 cells infected with PRRSV or treated with PRRSV-positive exosomes. (C) PK-15CD163 and Marc-145 cells were infected with PRRSV or treated with purified PRRSV-positive exosomes, and the viral titers were determined with TCID50 assay. (D) PK-15 cells were incubated with PRRSV-positive exosomes or infected with PRRSV at an MOI of 1.0. Pseudorabies virus (PRV) was used as the positive control for infection of PK-15 cells. At 36 h after treatment or infection, cells were fixed and IFAs were performed with MAb directed against PRRSV N protein or PRV gD. (E) Western blot analysis of PRRSV N protein expression in PK-15 cells infected with PRRSV or purified PRRSV-positive exosomes. DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.