FIG 6.
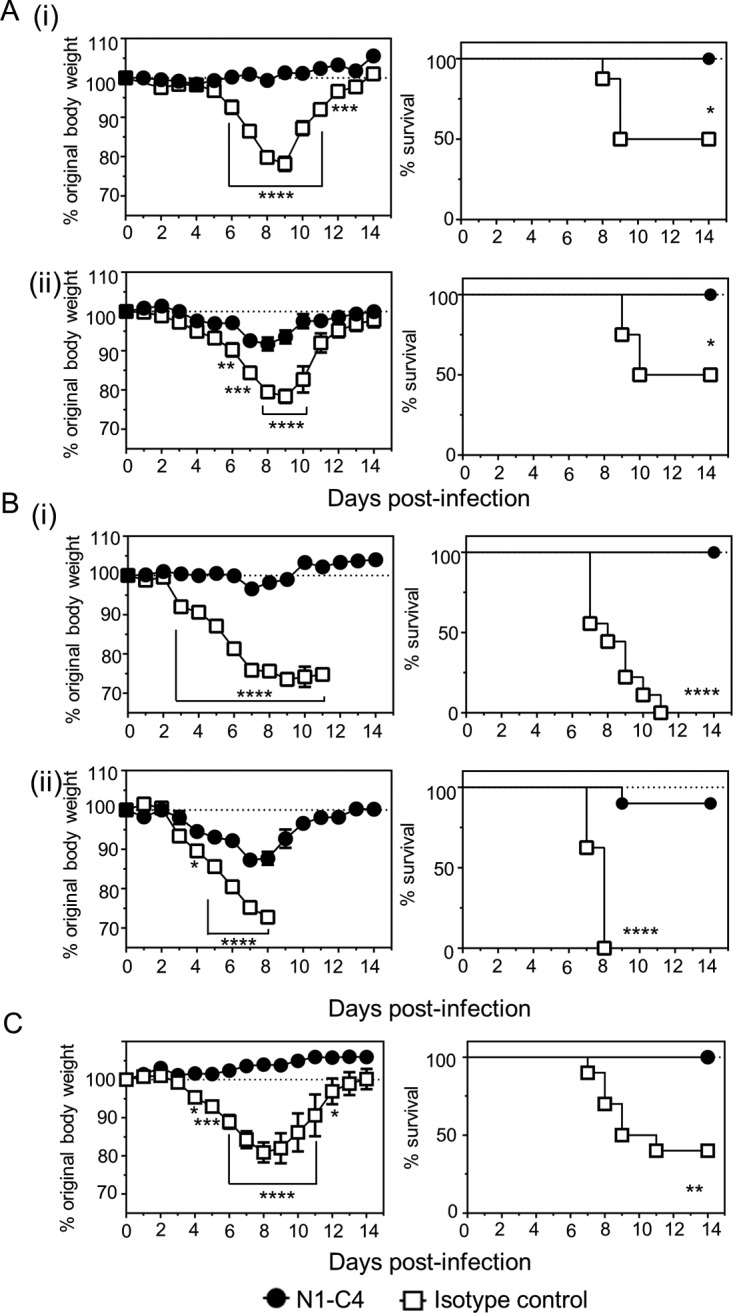
Treatment of mice with N1-C4 protects against lethal infection with H1N1 or H5N1 IAV. (A and B) BALB/c mice were treated with 20 μg of N1-C4 or an isotype control via the intranasal route under isoflurane sedation. The following day, the mice were infected with 1 LD50 (A) or 4 LD50 (B) of Bel/09 (i) or NIBRG-14 (ii) and monitored daily for weight loss (left) and survival (right). (C) Therapeutic treatment of mice with N1-C4 ameliorates disease induced by Bel/09. BALB/c mice were infected via the intranasal route with 1 LD50 of Bel09. Monoclonal antibody N1-C4 (200 μg) was administered by the i.p. route on days 1, 3, and 5 postinfection. A group of mice received an isotype control. The mice were monitored daily, and any mice that had lost ≥25% of their original body weight were euthanized. The weight loss data represent the mean percentages (± standard errors of the mean [SEM]) of original body weight over time (n = 8), and the survival data are shown as percent survival over time (n = 8). Weight loss over time was analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction, and survival proportions were assessed using a two-tailed log rank (Mantel-Cox) test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.
