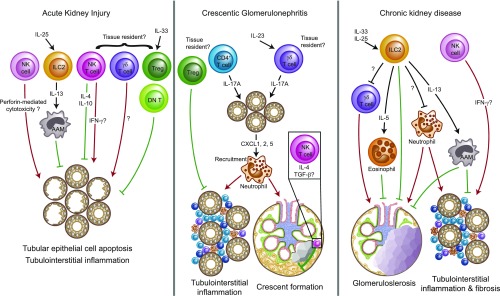
Figure 3.
Tissue-resident lymphocytes are likely to play important roles in renal disease. Graphic summary of the so far identified functions of potentially tissue-resident innate, innate-like, and adaptive lymphocyte populations in AKI induced by ischemia and reperfusion,32,36,40,45,65,66,73 crescentic GN,44,48,51,57–59 and chronic progression of kidney disease.34,35 The tissue residency of a subset of NK cells32 and the presence of conventional Trm cells8,17,72 in the murine kidney have been clearly shown (Table 1). Given the results from other organs, the existence of kidney-resident subsets among renal γδ T cells, ILCs, NKT cells, and CD4+ T cells can be assumed. However, the formal experimental proof of this hypothesis is still lacking. Red arrows depict proinflammatory mechanisms that promote disease progression, whereas green symbols represent anti-inflammatory effects that dampen tissue damage. AAM, alternatively activated macrophages; DN T, double-negative T cell, Treg, regulatory T cell.