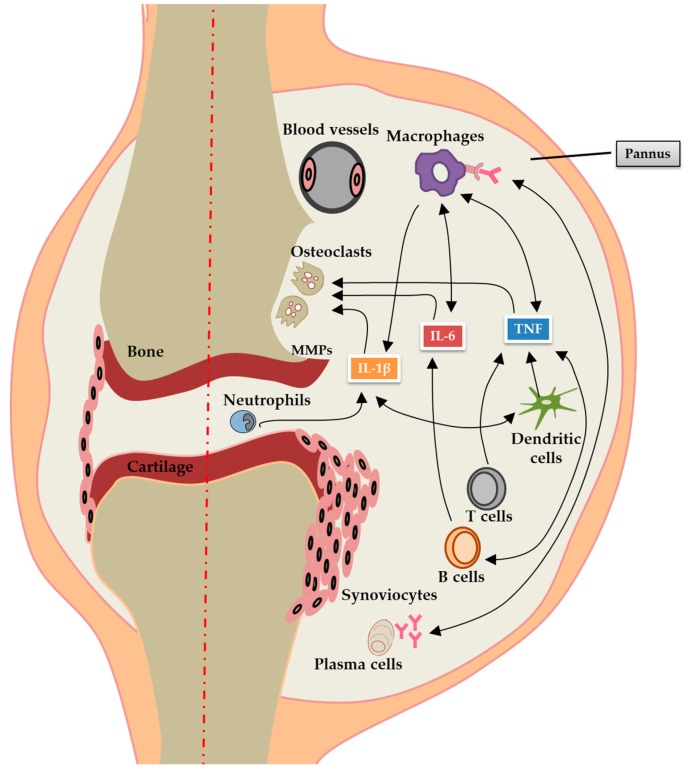
Figure 1.
Pathogenesis of RA: pannus formation and systemic inflammation. Inflammation in RA is caused by activation of B cells, T cells, plasma cells, neutrophils, dendritic cells and macrophages, which releases proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. These cytokines cause local joint damage through increased production of MMPs and activation of osteoclasts. TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 also leak out to the blood stream resulting in systemic inflammation. TNF, tumor necrosis factor; IL, interleukin; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases.