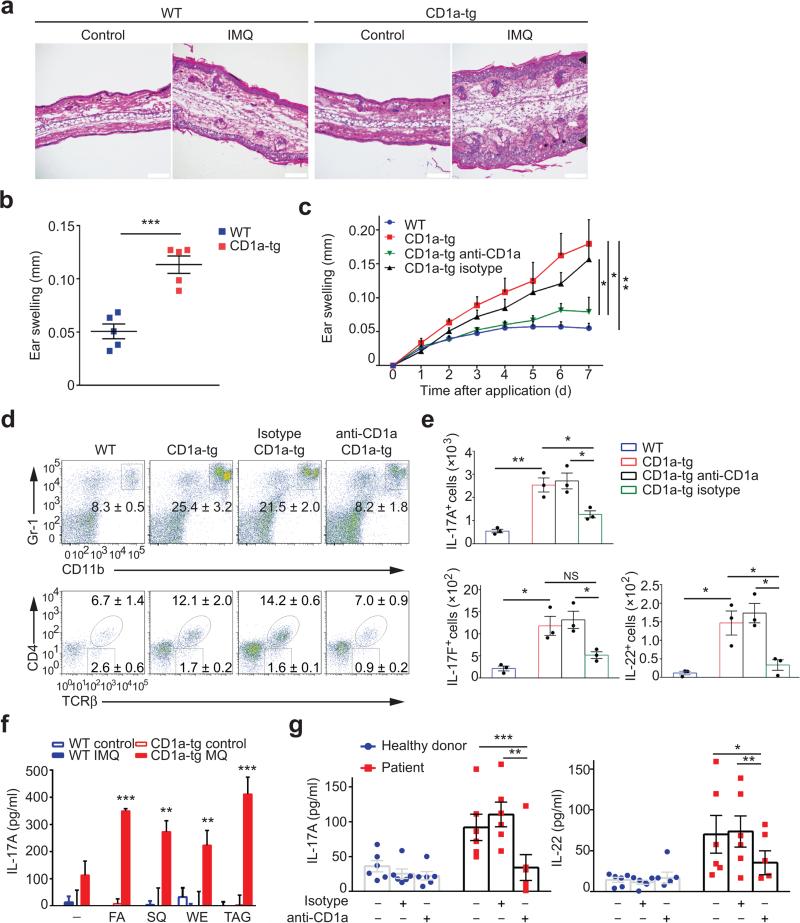
Figure 8.
CD1a is a novel target for treatment of psoriatic inflammation. (a) Microscopy of hematoxylin and eosin stained cross-sections of ears applied with Imiquimod (IMQ) for 6 days. Black arrows indicate epidermal thickening. Scale bar: 100 μm. (b) Ear swelling in mice (n = 5 per group) treated as in a. (c) Ear swelling of IMQ-treated wild-type (n = 8), CD1a-tg (n = 8), or CD1a-tg mice injected with anti-CD1a (n = 8) or isotype (n = 6). (d-e) Frequencies of Gr-1hiCD11bhi granulocytes and TCR-β+CD4+ cells among live CD45+ cells (d), and absolute cell numbers of IL-17A-, IL-17F-, and IL-22-producing CD4+ T cells (e) in ear skins of mice treated as in c (n = 3 per group). (f) Concentration of IL-17A in supernatants from dLN CD4+ T cells (n = 3) isolated from mice treated or non-treated with IMQ, and stimulated by plate-bound CD1a loaded with fatty acid (FA), squalene (SQ), wax ester (WE), or triacylglycerol (TAG). (g) Concentration of IL-17A and IL-22 in supernatants from CD45RO+ memory T cells isolated from patients with active psoriasis (n = 6), or healthy donors (n = 6), and cocultured with autologous monocyte-derived DCs in the presence of anti-CD1a or isotype. Each symbol represents an individual subject (b,e,g). Data shown are the mean ± s.e.m. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001, **** P<0.0001, using unpaired t-test (b,f), two-way ANOVA (c), and one-way ANOVA (e,g). Data are representative of five (b), or three independent experiments (c-f).