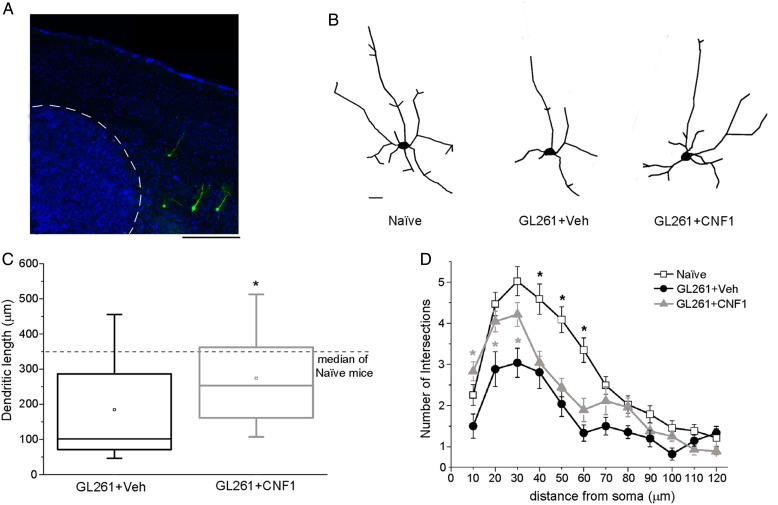
Fig. 6.
CNF1 counteracts the impaired dendritic branching in glioma-bearing mice. (A) Representative Thy1-GFP neurons (green) in a Hoechst-stained coronal section through the mouse primary visual cortex. Tumor borders are indicated by the dotted line. Dorsal is up and lateral is to the right. Scale bar = 500 µm. (B) Neurolucida tracings of representative Thy1-GFP pyramidal neurons in naïve, vehicle-, and CNF1-treated glioma-bearing animals. Scale bar = 10 µm. (C) Box charts showing total dendritic length for neurons from glioma-bearing mice. The horizontal dotted line represents the median value observed in naïve mice for comparison. Dendritic length is significantly increased in CNF1- vs vehicle-treated mice (Mann–Whitney rank sum test, *P < .05). (D) Sholl analysis of layer V pyramidal neurons in naïve, vehicle-, and CNF1-treated glioma-bearing mice. CNF1 treatment maintains a higher number of intersections close to the cell soma (2-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Holm–Sidak test, 10-20-30 µm from soma, CNF1 vs vehicle, *P < .05). Data are mean ± SEM.