Figure 12. Synthesis of Core MNPs.
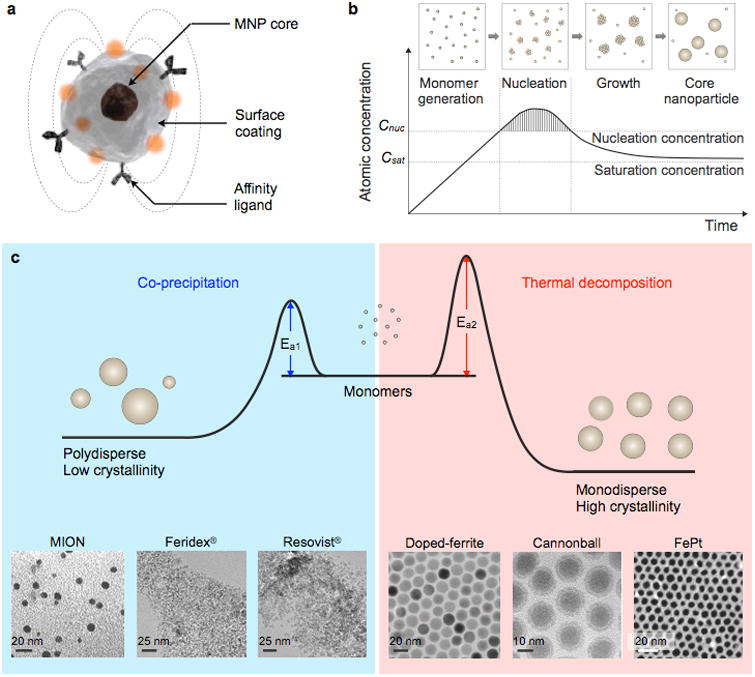
(a) Representative structure of a MNP. (b) Crystal-growth diagram. When the monomers are supersaturated and exceed the nucleation concentration, seed nucleation is induced and monomers are continuously aggregated onto the seeds, leading to crystal growth. Cnuc, nucleation concentration; Csat, saturation concentration. (c) Comparison of co-precipitation and non-hydrolytic thermal decomposition methods. The co-precipitation method results in kinetically favored MNPs which generally have a polydisperse size and relatively low crystallinity. Conversely, the thermal decomposition method produces thermodynamically stable MNPs with a monodisperse size and high crystallinity.Examples of transmission electron microscope (TEM) images of MNPs synthesized by co-precipitation (MION, Feridex®, Resovist®) or thermal decomposition methods (Doped-ferrite, Cannonball, FePt) are shown. Reprinted with permission from Ref. 155. Copyright 2014 Nature Publishing Group. Reprinted with permission from Ref. 175. Copyright 2012 American Institute of Physics. Reprinted with permission from Ref. 216. Copyright 2004 American Chemical Society.
