Figure 2. MicroNMR (μNMR) magnetometer.
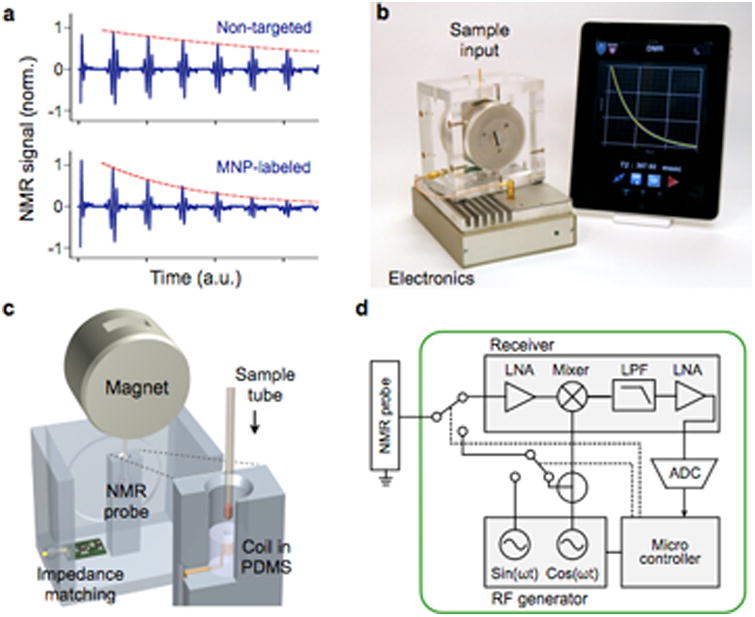
(a) Sensing mechanism. Samples containing MNP-labeled biological targets have higher transverse relaxation rate of 1H NMR signal. (b) Prototype portable μNMR system, developed for clinical applications. This system has a capacity for automatic system tuning and features a user-friendly interface. (c) Magnet assembly and the NMR probe design. The microcoil is embedded in a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) substrate. The entire coil-bore is accessible by a sample, which maximizes the sample-filing factor. A thin-walled tube is used for sample-loading. (d) The NMR electronics is implemented using a field-programmable-gate-array (FPGA) chip that offers standalone operation and high programability. LNA, low-noise amplifier; LPF, low-pass filter; ADC, analog-to-digital converter. Reproduced with permission from Ref. 45. Copyright 2011 RSC Publishing.
