Figure 4.
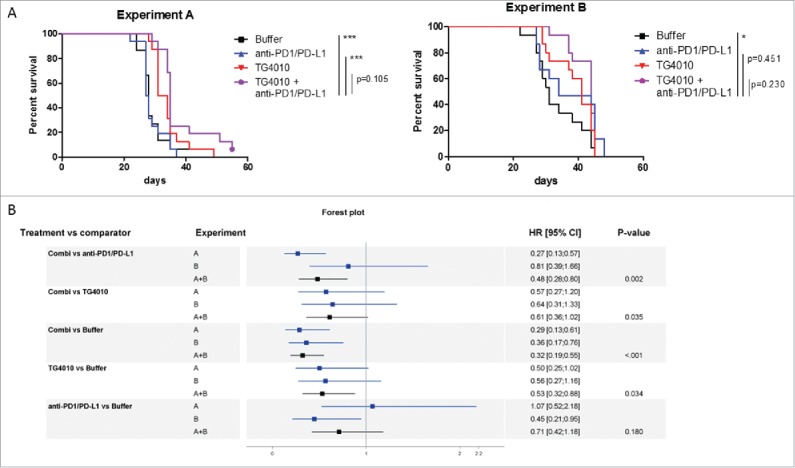
Effect of the sequential administration of anti-PD-1/anti-PD-L1 in the CT26-MUC1 model. (A) Groups of fifteen CT26-MUC1-injected mice were treated with TG4010 (IV injection of 5 × 107 pfu) at day 2 and day 9, followed by intraperitoneal injection of 250 µg of anti-PD-1 (clone RMP1.14) and 200 µg of anti-PD-L1 (clone 10F.9G2) at day 20, 24, 28 and 31. Survival was followed and criteria of sacrifice were based on weight loss. Two independent preclinical experiments (A and B) showed a trend of better overall survival for mice receiving the combination treatment. By combining the two experiments, a measurable benefit on tumor onset and survival was found for mice receiving both TG4010 and anti PD-1/PD-L1 versus monotherapy. (B) Forest plot analysis: the hazard ratio (HR) derives from the unstratified Cox proportional hazards model for experiments A and B. Meta-analysis was done for A+B with a fixed effect model by weighting estimates with the inverse of variance. The p-value was obtained using a stratified log-rank test for comparing survival curves. Animal experiments were conducted in compliance with EU directive 2010/63/EU.
