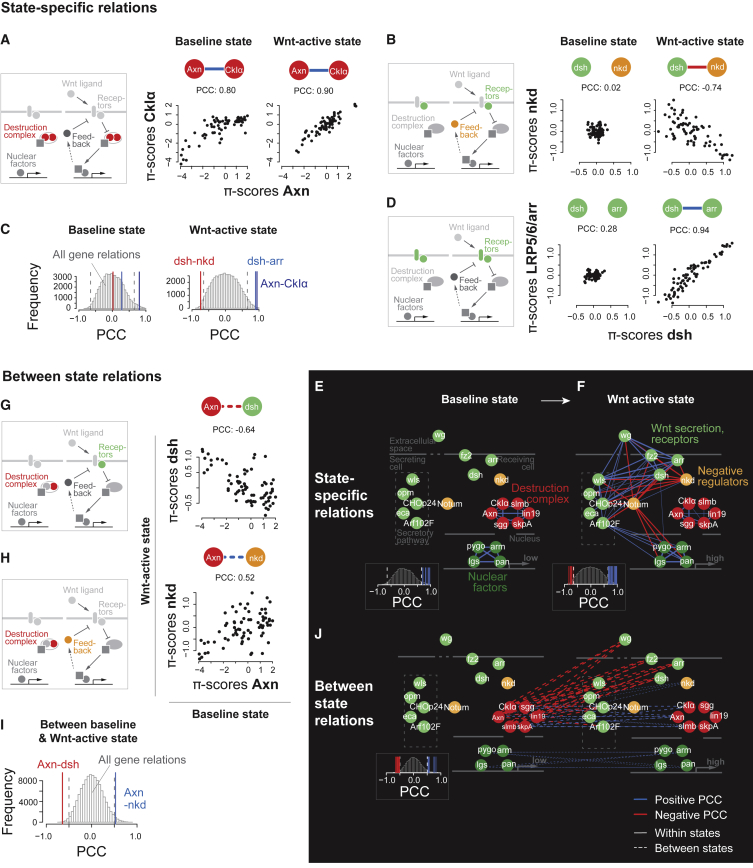
Figure 2.
Between-State and State-Specific Functional Relations Visualize Change of Gene Function and Rewiring of the Core Wnt Signaling Network
(A–D) State-specific correlation between genetic interaction profiles of the destruction complex components Axn and CkIα (both states: p < 2.2e−16, Pearson product-moment correlation) (A), dsh and nkd (baseline: p = 0.88; Wnt-active: p = 8.5e−14) (B) or receptor complex components LRP5/6/arr and dsh (baseline: p = 0.02; Wnt-active: p < 2.2e−16) (D) in the baseline and Wnt-active state. Each profile contains 72 quantitative genetic interaction (π) scores. (C) Correlation coefficients from (A), (B), and (D) in relation to the 56,280 measured coefficients in each respective state.
(E and F) State-specific correlation-based networks connecting core Wnt pathway components involved in ligand secretion and receptor complex binding (green), negative feedback (orange), the destruction complex (red), or target gene transcription (dark green) in baseline (E) or Wnt-active (F) states. The similarity or dissimilarity of each gene pair was estimated by computing Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) between the genetic interaction profiles. Genes with an absolute PCC > 0.65 were connected. The edge width represents the absolute value of the coefficient; the color indicates positive (blue) or negative (red) correlation.
(G–I) Between-state correlation between genetic interaction profiles of Axn and dsh (p = 1.08e−9) (G), or Axn and nkd (p = 2.13e−6) (H). (I) Correlation coefficients from (G) and (H) in relation to the 112,896 measured coefficients between baseline and Wnt-active state.
(J) Between-state correlation-based network connecting core Wnt pathway components involved in ligand secretion and receptor complex binding (green), negative feedback (orange), the destruction complex (red), or target gene transcription (dark green) between baseline and Wnt-active state. Genes with an absolute PCC > 0.5 were connected.