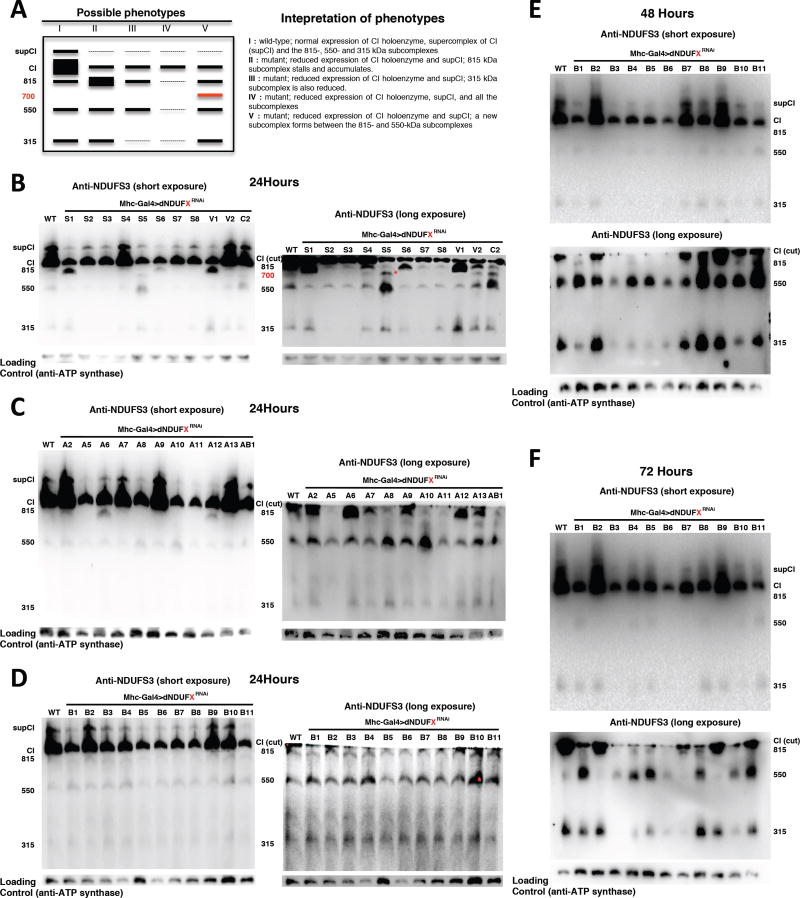
Figure 4. Specific Subunits Regulate the Biogenesis or Stability of Specific Assembly Intermediates Of CI.
(A) The left panel depicts a schematic of the distribution of assembly intermediates on immunoblots as a result of RNAi-mediated disruption of various CI subunits. The right panel describes how various results can be interpreted.
(B–D) Distribution of assembly intermediates in thoraxes dissected 24 hours after eclosion with transgenic RNAi expression of the CI subunits shown. The ~815 kDa assembly intermediate accumulates in thoraxes expressing transgenic RNAi to dNDUFS1, dNDUFV1, dNDUFA6 and dNDUFA12; the ~315 kDa assembly intermediate is decreased in thoraxes expressing transgenic RNAi of dNDUFS2, dNDUFS3, dNDUFS7 and dNDUFA5. In addition, another assembly intermediate accumulates in thoraxes expressing RNAi to dNDUFS5 and dNDUFC2 (denoted by * in B). In panels labeled long exposure, the region of the membrane just at or below CI was cut and imaged.
(E and F) Distribution of assembly intermediates in thoraxes dissected 48 hours (E) and 72 hours (F) after eclosion with transgenic RNAi expression of the NDUFB subunits shown. RNAi-mediated knockdown of the expression of dNDUFB3 decreased the extent of accumulation of all the assembly intermediates; and the 550 kDa assembly intermediate accumulated when the expression of dNDUFB1, dNDUFB8 and dNDUFB11 were reduced. In addition, the extent of accumulation of the 315 kDa assembly intermediate was diminished following RNAi-mediated disruption of dNDUFB1, dNDUFB4, dNDUFB5, dNDUFB6 and dNDUFB10.