Figure 1.
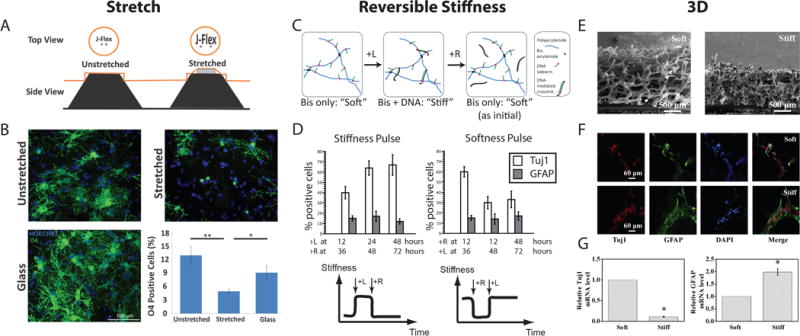
Novel material platforms have been used to investigate NSC mechanosensitive differentiation. The “J-Flex”, a tension-based stretch culture system (A), shows that a stretch cue decreases oligodendrocytic differentiation (O4 marker staining) and is independent from stiffness inputs (B). A DNA-crosslinked polyacrylamide gel system enables reversible stiffness tuning (C), which reveals a 12–36 hour time window for mechanosensitive fate commitment in NSCs (D). Stiffer graphene-based 3D materials (E) decrease neurogenesis (Tuj1) and increase astrocytic differentiation (GFAP) as measured by staining (F) and qPCR (G). Reproduced with permission from [33], [16], and [57].
