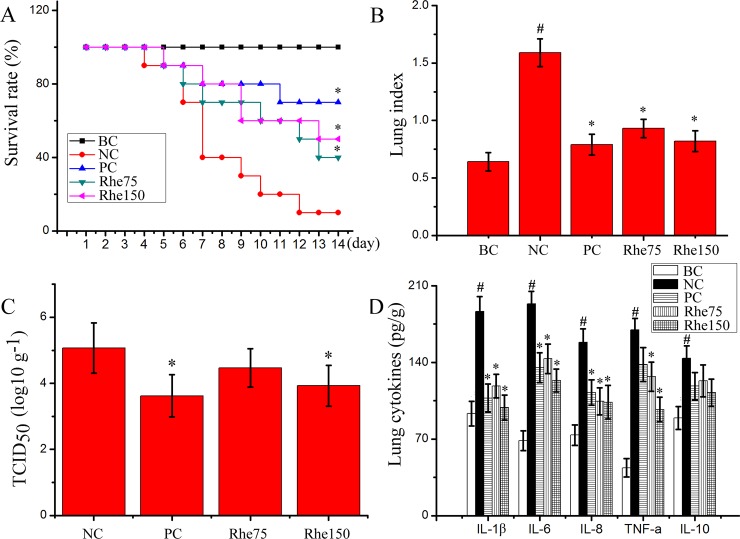
Fig 6. Anti-IAV activity of rhein in mice.
In the blank control (BC), mice were not infected with IAV (PR8) but shammed with VGM medium and treated with DMSO (0.5%). In the negative control (NC), positive control (PC), and rhein-treated groups (Rhe75 and Rhe150), mice were infected with 10× MLD50 of IAV (PR8) and treated with DMSO (0.5%), oseltamivir (10 mg/kg/day) and rhein (75 mg/kg/day and 150 mg/kg/day), respectively. (A) The survival rate was observed for 14 days and analyzed by using Kaplan-Meier analysis with Log-rank and Breslow tests. (B) The lung index was assessed by determining the percent of lung wet weight (g) to body weight (g) (lung index = lung wet weight (g) ÷ body weight (g) × 100%). (C and D) The pulmonary viral load and cytokines were determined by TCID50 and ELISA assays, respectively. Data were mean ± SD. Ten mice were used in the survival rate assay (n = 10) and six mice were used in the lung index, pulmonary viral load, and pulmonary cytokines assays (n = 6). #P < 0.05 vs. the BC group, *P < 0.05 vs. the NC group.