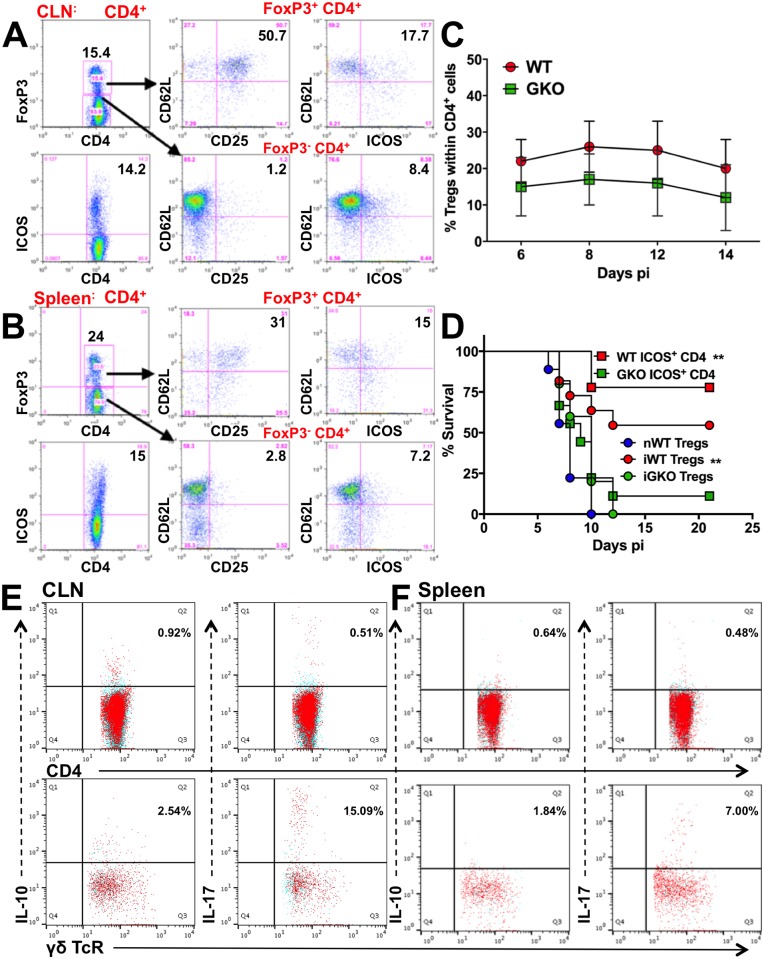
Fig 4. Regulatory CD4 T cells are impaired in the absence of IFNγ.
FoxP3+ (top) and ICOS+ (bottom) CD4 T cells (left) in (A) CLN and (B) spleen of WT mice at day 8 pi. FoxP3+ (top row) and FoxP3- (bottom row) CD4 T cells probed for CD62L and CD25 expression (middle) and ICOS expression (right). (C) % FoxP3 Tregs within splenic CD4 T cells isolated from WT or GKO mice at the indicated time points; data representative of 2–3 experiments are shown as mean ± SD. (D) FoxP3+ CD25+ CD4 T cells (Tregs, 5x106) or ICOS+ (107) CD4 T cells isolated from naïve WT (nWT), infected WT (iWT) or GKO (iGKO) mice at day 8 pi were adoptively transferred to naïve WT recipients, which were then challenged with HSV but did not receive IVIG, and monitored for survival (n = 6–8 mice). **p = 0.002. CD4 (top row) or γδ (bottom row) T cells isolated from (E) CLN or (F) spleen of GKO mice at day 6 pi were probed for IL-10 and IL-17 by ICS. Blue dots indicate no antigenic stimulation; red dots indicate cells stimulated with PMA + ionomycin + heat-killed HSV (HK-HSV).