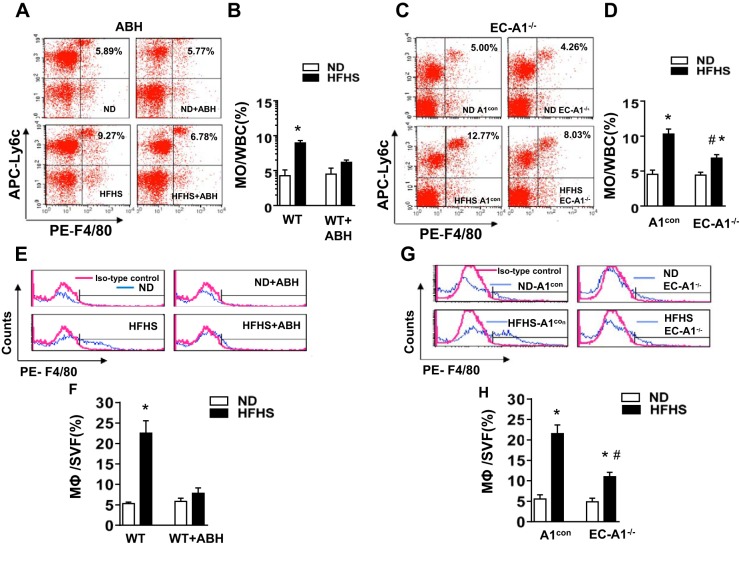
Fig. 4.
Arginase inhibition or EC-A1 deletion prevents or blunts the HFHS-induced increases in circulating inflammatory monocytes and limits macrophage infiltration into stromal vascular fraction of visceral adipose tissue. Representative FACS profile showing effects of ABH (A) or EC-A1 deletion (C) on the percentage of circulating white blood cells (WBC) with high levels of both Ly6C and F4/80. APC, allophycocyanin; PE, phycoerythrin. Histograms show the percentage of Ly6Chigh/F4/80high inflammatory monocytes (MO) in total circulating blood cells (B and D). Representative FACS profile showing effects of ABH (E) or EC-A1 deletion (G) on percentage of macrophages (F4/80high) within the stromal vascular fraction (SVF). Histograms show the percentage of macrophage (MΦ) cells in the SVF (F and H). Values are means ± SE; n = 5–7 mice. *P < 0.05 vs. WT ND or A1con ND groups. #P < 0.05 vs. WT HFHS or A1con HFHS groups.