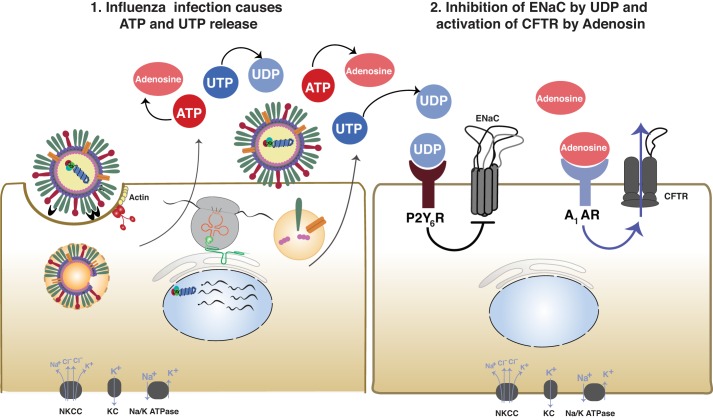
Fig. 5.
Influenza virus alteration of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) and epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) activity through the release of ATP/UTP. After influenza infection, both ATP and UTP were significantly increased 1 and 2 days postinfection due to viral infection of the lung epithelium. UTP is hydrolyzed to UDP and acts on the P2Y6R receptor, leading to decreased amiloride-sensitive ion transport. Simultaneously, ATP is hydrolyzed to adenosine, which acts on the A1-AR. Activation of the A1-AR increases Cl− secretion through CFTR. The combination of decreased Na+ absorption and increased Cl− secretion leads to increased airway surface fluid and pulmonary edema. This is based on conclusions previously published (109). NKCC, Na+/K+/2Cl−; KC, K+ channels.