Figure 2. Representativebioactive small compounds exhibit mitochondrial benefits.
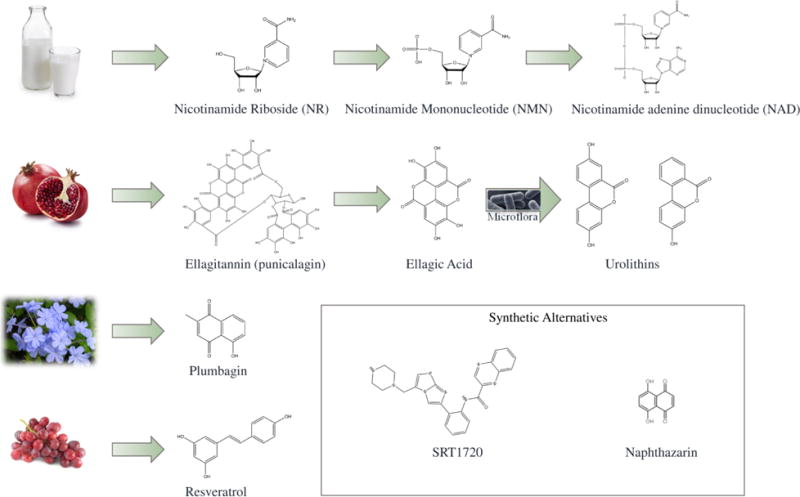
Many of these naturally-occurring compounds are derived from common foods, such as milk,pomegranate, plumbago and grapes. Phytochemicals can be innately synthesized by the plant, such as the case for plumbagin and resveratrol. They can also be metabolized in the body to produce the potential anti-sarcopenic compound, such as the metabolism of NR to NAD+, or the conversion of ellagitannins to urolithins with help of intestinal microflora. Synthetic derivatives of naturally-occurring compounds are also effective in modulating mitochondrial function through similar mechanisms, which is seen with the resveratrol-derived SRT1720 or the plumbagin-derived naphthazarin.
For images used here, Milk: Krans, B. (2014). “Almond Milk vs. Cow Milk vs. Soy Milk vs. Rice Milk”; Promagranate: TrimDownClub (2015). “10 Things We Love About Pomegranates (Plus Pomegranate Recipes)”; Plumbago: brewbooks (2005). Plumbagoauriculata. Wikimedia Commons; Grapes: Council, C. N. C. (2012). “Chicken With Grapes and Rosemary Recipe.”
