Figure 7.
Synaptically Efficient Optogenetic Stimulation of the Septo-habenular Pathway Induces Anxiolysis and Increases Mouse Mobility
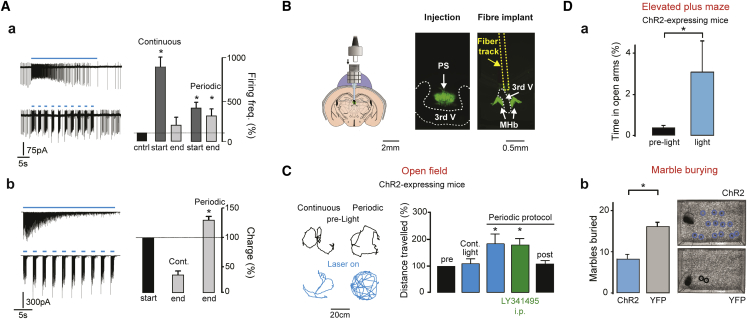
(A) Continuous optogenetic stimulation (30 s, 20 Hz) rapidly lost efficiency at increasing firing of MHb cells in LCA recordings. The response of a typical neuron is illustrated (top left; quantification in the right graph). In contrast, periodic laser-on (1 s)/laser-off (2 s) trains quantitatively maintained their effect over long periods (bottom traces and bar graph). Firing was quantified in the first (start) and last (end) 4 s of stimulation as percentage of control spike rate. (b) In the whole-cell configuration, dramatic synaptic fatigue developed rapidly during continuous trains but not during periodic stimulation, consistent with the results shown in (a). The charge transferred at stimulation end was quantified as a percentage of the charge obtained at train onset.
(B) For in vivo optogenetic experiments, injected mice (see center for fluorescence at the PS injection site of one mouse) were implanted with a fiber optic just above the MHb, as shown schematically on the left and for one animal on the right (the fiber track is highlighted in yellow).
(C) Intermittent stimulation in freely moving, ChR2-expressing VGluT2-Cre mice robustly increased locomotion. In contrast, continuous trains did not produce significant changes in the total distance traveled (quantified in the right bar graph). Mouse position in the open-field arena in time is shown for one animal before (left black traces, corresponding to 1-min-long period) and during stimulation (bottom, blue) for continuous (left) and periodic (right) trains. The effect on locomotion of the intermittent protocol was also maintained following intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of LY341495 (quantifications shown in the right bar graph). Light trains produced no significant change in locomotor activity in VGluT2-Cre mice expressing only eYFP at PS inputs (data not shown).
(D) PS input activation in the MHb is anxiolytic. (a) ChR2-expressing mice spent more time in the open arms of an EPM during optogenetic stimulation (blue bar) than in the pre-light period (black). (b) ChR2-YFP expressing mice buried significantly fewer marbles than animals expressing only YFP (quantified in the left graph). The images illustrate the unburied marbles for 2 mice.
Pooled data are represented as mean ± SEM.