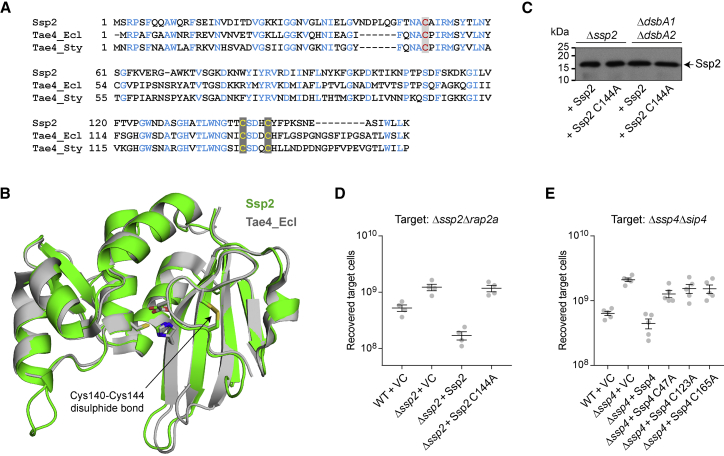
Figure 5.
Disulfide Bond Formation in Ssp2 Is Required for Toxicity but Not Stability
(A) Sequence alignment of Ssp2 from S. marcescens Db10 (SMDB11_2264), Tae4 from Ent. cloacae (Tae4_Ecl; UniProt: A0A0H3CIJ2), and Tae4 from Sal. Typhimurium (Tae4_Sty; UniProt: Q93IS4). The catalytic Cys residue is shown in red, and the pair of Cys residues indicated to form a disulfide bond are shown in yellow.
(B) Structural alignment of Tae4_Ecl (gray) with a model of Ssp2 (green). The Ssp2 model was generated based on the structures of Tae4_Ecl (PDB: 4HFL) and Tae4_Sty (PDB: 4J32) using iTASSER (C score 1.25, TM score 0.89 ± 0.07), with further refinement by molecular dynamics simulation. Residues involved in the disulfide bond (Ssp2 Cys140-Cys144) or catalytic triad (Ssp2 Cys50, His131, Asp142) are shown as sticks.
(C) Immunoblot detection of wild-type Ssp2 and Ssp2 C144A in the total cellular fraction of Δssp2 or ΔdsbA1ΔdsbA2 strains of S. marcescens Db10. Expression of Ssp2 and Ssp2 C144A was from pSUPROM-based plasmids pSC1588 (+Ssp2) and pSC1589 (+Ssp2 C144A), respectively.
(D) Recovery of target strain Δssp2Δrap2a following co-culture with wild-type (WT) or Δssp2 mutant S. marcescens Db10 carrying the vector control (+VC) or plasmids directing the expression of Ssp2 and Ssp2 C144A. Individual data points are overlaid with the mean ± SEM (n = 4).
(E) Recovery of target strain Δssp4Δsip4 following co-culture with wild-type or Δssp4 mutant Db10 carrying the vector control (+VC, pBAD18-Kn) or plasmids directing the expression of Ssp4 (+Ssp4, pSC836), Ssp4 C47A (+Ssp4 C47A, pSC1598), Ssp4 C123A (+Ssp4 C123A, pSC1599), or Ssp4 C165A (+Ssp4 C165A, pSC2500). Ssp4 variant expression was induced with 0.002% arabinose. Individual data points are overlaid with the mean ± SEM (n = 5).