Figure 3.
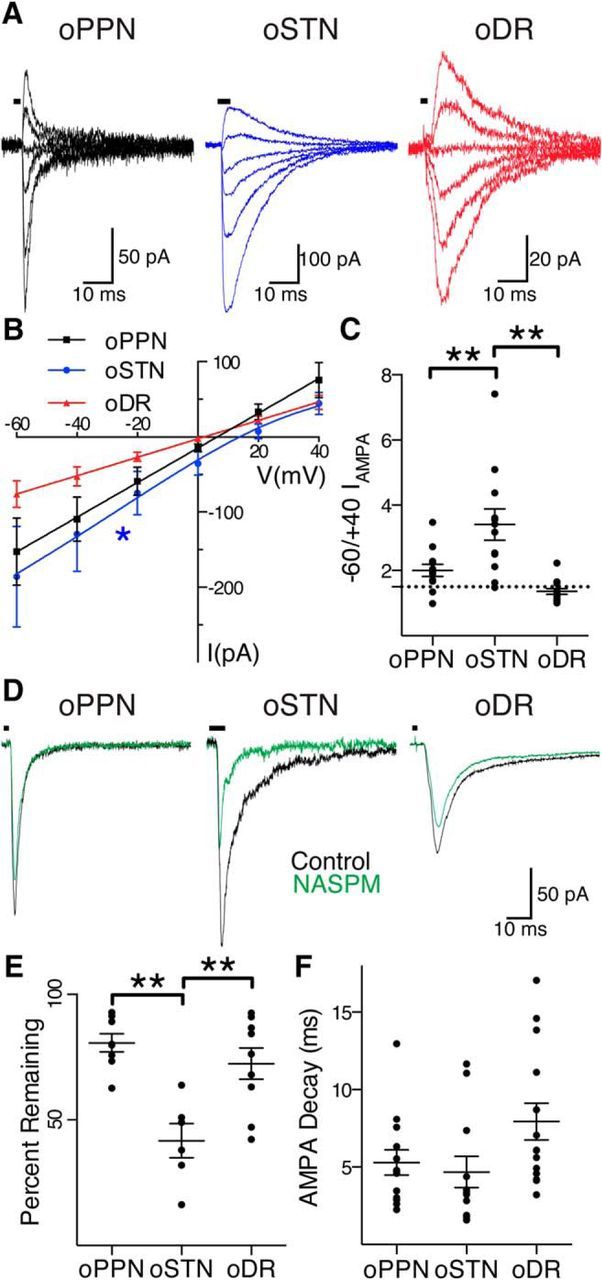
PPN, STN, and DR afferents activate different complements of AMPA receptors on dopamine neurons. A, oPPN-evoked (black), oSTN-evoked (blue), and oDR-evoked (red) AMPA receptor-mediated currents at holding voltages of −60, −40, −20, 0, +20, and +40 mV, from bottom trace to top trace. B, oPPN-evoked and oDR-evoked AMPA receptor-mediated currents (black and red) have a linear I–V relationship, indicating that they contain the GluA2 subunit. oSTN-evoked AMPA receptor-mediated current with inwardly rectifying I–V relationship (blue), not going through 0 pA, 0 mV. C, Rectification index corresponding to the ratio of currents at a holding voltage of −60 to +40 mV. The dashed line represents a ratio of 1.5, corresponding to a linear I–V relationship. D, oPPN evoked an inward current (black) that is marginally sensitive to NASPM (green). oSTN-evoked AMPA receptor-mediated current (black) is significantly inhibited by NASPM (green), indicating the presence of calcium-permeable AMPA receptors. oDR-evoked AMPA receptor-mediated current (black) is also partially inhibited by NASPM (green). E, Calcium-permeable AMPA receptor antagonists JTx and NASPM significantly decrease the normalized amplitude of AMPA receptor-mediated currents from oSTN compared with oPPN and oDR. F, The time constant of decay for AMPA receptor-mediated currents produced at a holding voltage of −60 mV. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
