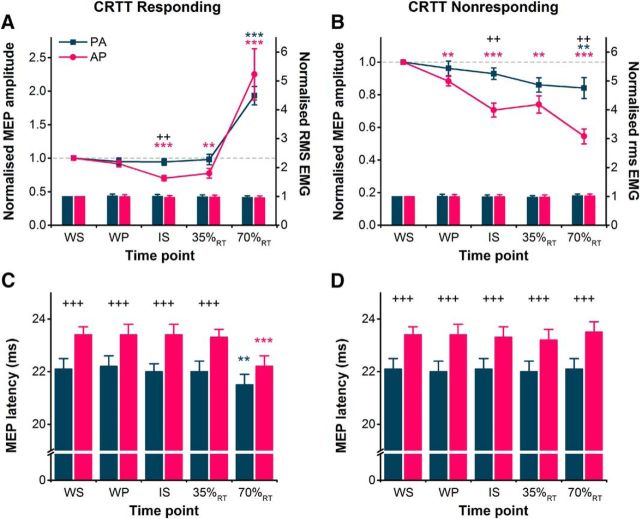
Figure 3.
A, B, During the choice reaction time task, MEP amplitudes in the right FDI shown normalized to the WS time point (colored lines, left y-axis) were suppressed more for AP currents than for PA currents at the IS during right hand-responding trials (A) and at the IS and 70%RT in right-hand nonresponding trials (B). The facilitation of MEPs in right hand-responding trials at 70%RT was similar for both current directions (A). Voluntary rms EMG (colored bars, right y-axis) measured before the TMS pulses is shown normalized to values at the WS, and was similar for PA and AP currents across different time points for right hand-responding (A) and nonresponding trials (B). C, D, MEP latencies were longer for AP currents compared with PA currents in both right hand-responding (C) and nonresponding (D) trials at all time points except 70%RT in responding trials. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, compared with the WS time point within each current direction; ++p < 0.01, +++p < 0.001, AP vs PA.