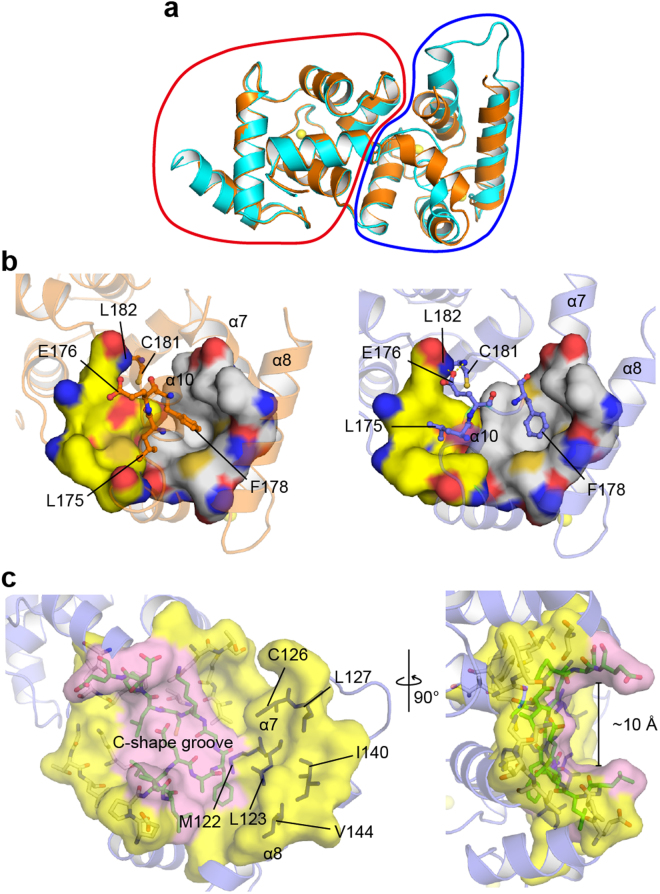
Figure 2.
Structural basis for the open-closed transition of calaxin. (a) Structural comparison between the open state (cyan) and closed state (orange) in the Ca2+-bound form. The N-terminal domains and C-terminal domains are circled by a red line and a blue line, respectively. (b) Structures of Ca2+-bound calaxin in the closed (left) and open (right) states. Stick models indicate the residues critical for the twist of EF-hand motifs in the process of the open-closed transition. Hydrophobic holes for F178 and L175 binding are indicated by white and yellow surfaces, respectively. (c) Exposed surface of calaxin in the open state. The C-shaped groove (pink surface) is highlighted in pink, and residues forming the groove are colored green. Residues on the exposed surface and twisted helices are shown by magenta sticks and slate ribbon, respectively.