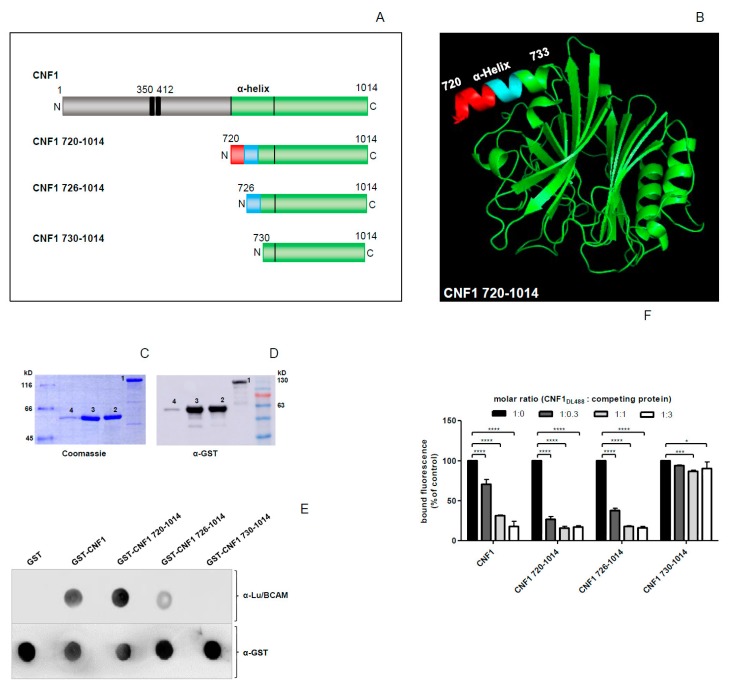
Figure 1.
Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor 1 (CNF1) 730–1014 shows no interaction, CNF1 726–1014 shows weaker interaction with rLu/BCAM in comparison to CNF1 and CNF1 720–1014. (A) Schematic representation of CNF1 and its truncated versions with the α-helix of interest highlighted; (B) crystal structure of the catalytic part of CNF1 from amino acid 720 to 1014, the α-helix of interest from amino acid 720 to 733 is highlighted; (C,D) enrichment of GST-CNF1 (1), GST-CNF1 720–1014 (2), GST-CNF1 726–1014 (3), and GST-CNF1 730–1014 (4) verified via SDS-PAGE following Coomassie staining (C) or an immunoblot using an anti-GST antibody (D); (E) dot blot binding analysis, different CNF proteins were dotted on a nitrocellulose membrane and incubated with rLu/BCAM for 30 min. After blocking the membrane with skimmed milk, detection of rLu/BCAM was performed with an anti-Lu/BCAM antibody; (F) flow cytometry competition studies, suspension of HeLa cells (3 × 105 cells in 1 mL medium) were preincubated with different unlabeled N-terminal truncated CNF1 proteins, respectively. Then, cells were washed with PBS and incubated with DyLight488-labeled GST-CNF1 (as control cells were incubated with labeled CNF1 without preincubation and set to 100%). Following washing with PBS, cells were subjected to flow cytometry measurements. The bound fluorescence is shown in comparison to the control. Data shown represent three independent experiments + standard deviations. Statistical analyses were performed using two-way ANOVA. * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.