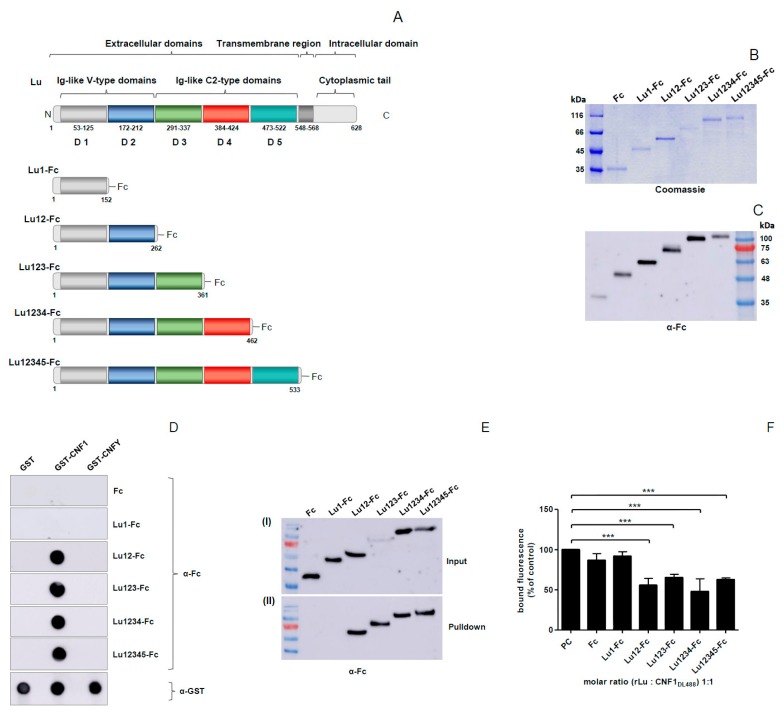
Figure 3.
Domain 2 of Lu/BCAM is involved in binding to CNF1. (A) schematic representation of Lu with its extracellular, transmembrane and intracellular part; (B,C) purification of different Lu-Fc proteins and verification via SDS-PAGE (B) and western blotting using an anti-Fc antibody (C); (D) dot blot interaction studies, different CNF proteins were dotted on a nitrocellulose membrane, following blocking of the membrane with skimmed milk. After incubation with different Lu-Fc proteins, respectively, the Lu-Fc proteins were detected using an anti-Fc antibody. GST and GST-CNFY were used as negative controls; (E) GST pulldown assay with cell culture supernatants of Lu-Fc expressing COS7 cells. Cell culture supernatants of Lu-Fc expressing COS7 cells were incubated with beads-coupled GST-CNF1, respectively. After washing, the beads-coupled proteins were eluted with Laemmli sample buffer and separated by SDS-PAGE. Co-immunoprecipitation of Lu-Fc proteins was detected using an anti-Fc immunoblot (II). As Input, samples from the cell culture supernatants were taken before incubation with beads (I); (F) flow cytometry binding studies, DyLight488-labeled GST-CNF1 was pre-incubated with different Lu-Fc proteins respectively followed by an incubation with a suspension of HeLa cells (3 × 105 cells in 1 mL medium). As positive control cells were incubated with DyLight488-labeled CNF1 without preincubation with Lu-Fc. After washing three times with PBS, cells were subjected to flow cytometry measurements. The bound fluorescence is shown in comparison to the positive control, which was set to 100%. Data shown represent three independent experiments + standard deviations. Statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA. *** p < 0.001.