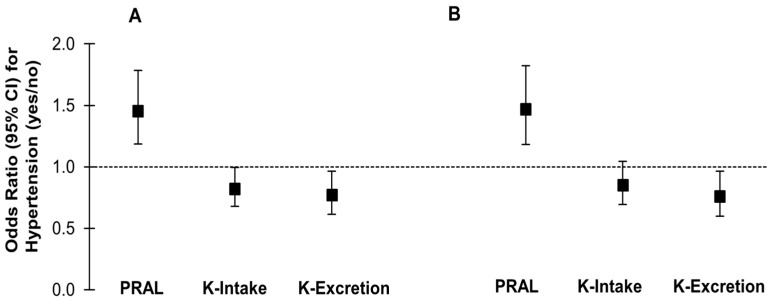
Figure 1.
Odds ratios (95% CI) for hypertension (yes/no) comparing the highest (T3) with lowest (T1) tertiles of potential renal acid load (PRAL), food frequency questionnaire-derived potassium intake (K-Intake), and potassium excretion in the total study sample (6765) (A) and in a subsample (n = 5854) (B) excluding participants with impaired renal function. Odds ratios were calculated using logistic regression models adjusted for age, sex, and body mass index, size of blood pressure cuff, fasting duration (> or <8 h), smoking status, natrium excretion, alcohol intake, estimated glomerular filtration rate, serum glucose, and total cholesterol. CI, confidence interval.