Fig. 2.
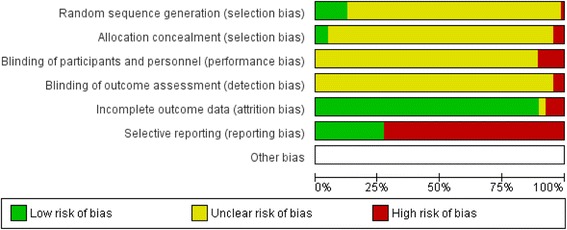
Risk of bias graph showing review authors’ judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies. Every publication included in the systematic review was assessed for its risk of bias based on the reporting of data. Randomized clinical trials had the lowest risk of bias. The large amount of unclear risk of selection, performance, and detection bias reflects the relatively large number of non-randomized observational studies in the systematic review. The relatively high risk of reporting bias is a reflection of data acquired from conference abstracts that were judged to have a higher risk of selective reporting than full literature articles
