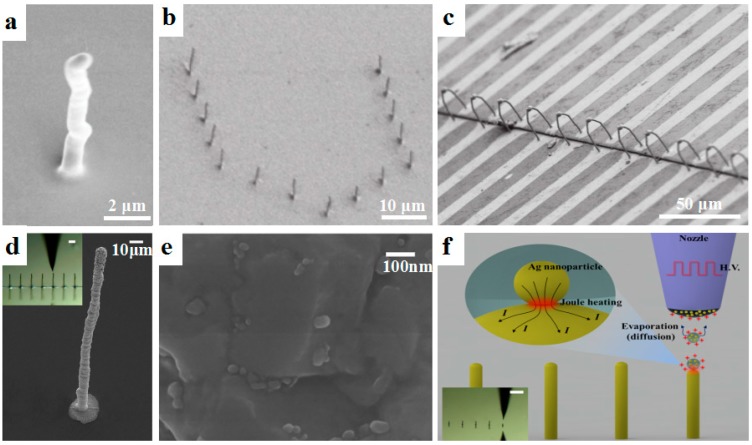
Figure 2.
Metal nanoparticles for the micro-/nano-scale 3D printing of conductive features. (a) Ag pillar printed by electrohydrodynamic 3D printing; (b) A “U-shaped” array of Cu; (c) “Bridge-like” Ag interconnects used as electrical connection of the two electrodes, reprinted from [19] with the permission of John Wiley and Sons, Copyright 2015; (d) SEM image of an electrohydrodynamically (EHD) printed sub-10 μm 3D pillar with high aspect ratio over 35. The inset is a photograph of the EHD printing process, and the scale bar is 30 μm; (e) The magnified surface morphology of the Ag nanoparticles on the 3D pillar structure; (f) Schematic of spontaneous nanoscale Joule heating in the fabrication of the high-aspect-ratio 3D structures for which the electrohydrodynamic 3D printing technique was employed, reprinted from [30] with the permission of John Wiley and Sons, Copyright 2017.