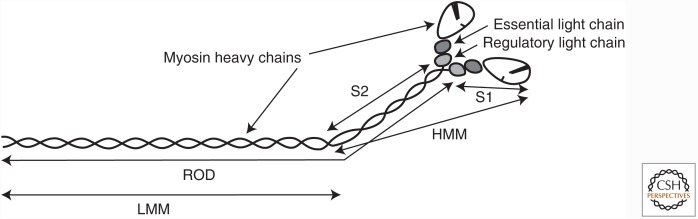
Figure 3.
The myosin molecule and its proteolytic fragments. Illustrated is the myosin molecule of muscle—myosin II—and the fragments that can be generated by limited proteolysis. The catalytic portion of the molecule is in the two enzymatically functional head (S1) fragments, each containing a nucleotide-binding site and an actin-binding site. The S1 fragment is commonly referred to as the “myosin head.” The remainder of the myosin molecule—the “rod”—comprising the amino-terminal portion (S2) and light meromyosin (LMM) fragments, forms an α-helical coiled coil. LMM forms the backbone of myosin filaments. A two-headed, catalytically active fragment of myosin known as heavy meromyosin (HMM) does not form filaments, and this serves a useful purpose for solution-biochemistry studies.