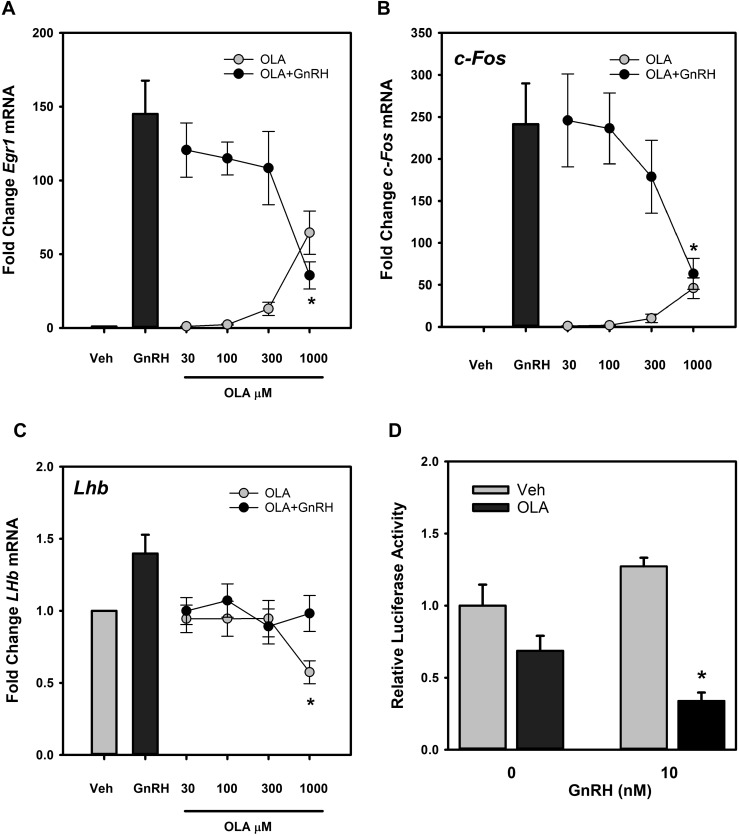
Figure 5.
OLA induces a dose-dependent increase in Egr1 and c-Fos mRNA but has no effect on Lhb mRNA. LβT2 cells were serum starved for 12 to 16 hours and subsequently treated for 3 hours with vehicle (Veh) or increasing doses of OLA alone or with the addition of 10 nM GnRH for the final 30 minutes and harvested. Total RNA was prepared and levels of Egr1, c-Fos, and Lhb mRNA were determined relative to Gapdh as an internal reference control. Values from three independent experiments are summarized in the histograms as fold change relative to untreated vehicle control samples. The results show that GnRH and OLA increase (A) Egr1 and (B) c-Fos, but cotreatment results in a dose-dependent suppression of mRNA relative to GnRH treatment alone. (C) OLA suppresses Lhb mRNA levels at the 1000-μM dose and limits responsiveness to GnRH. *Significant difference from untreated control as determined by Student t test. (D) OLA suppresses Lhb promoter activity in LβT2 gonadotropes. Cells transfected with a 1.8-kbp rat Lhb promoter-driven luciferase reporter gene and a cytomegalovirus promoter–based β-galactosidase reporter gene as an internal control were treated with vehicle or 500 μM OLA for 30 minutes and then stimulated with the addition of 10 nM GnRH for 4 hours. Cells were harvested, and luciferase activity was measured and normalized to β-galactosidase activity. The chart represents the ratio of luciferase to β-galactosidase activity. Error bars denote standard error of the mean of at least three independent experiments. *Represents significant difference between OLA and corresponding vehicle-treated controls.